Exercises in C++ Prime 5
Exercise section 不可照抄
Reference linking 1
Reference linking 2
第一章 1.9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;int main () int i = 50 ; int ans = 0 ; while (i <= 100 ) ans = i++; cout << ans; return 0 ; }
1.10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;int main () int i = 10 ; while (i >= 0 )cout << i-- <<" " ; return 0 ; }
1.11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;void swap (int &a,int &b) int t = a; a = b; b = t; } int main () printf ("please input two integers\n" ); int i, j; cin >> i >> j; if (i > j) swap(i,j); while (i <= j) cout << i++ << " " ; return 0 ; }
1.12 1 2 3 int sum = 0 ;for (int i = -100 ; i <= 100 ; ++i) sum += i;
1.14 实际上表达能力是一样的, 如果按照规范来写for循环,可以尽量缩小局部变量的作用范围.
for 循环和 while 循环会在 loop statement 前多做一次 conditional jump, do while 则不会.
1.16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;int main () int sum = 0 ; int num; while (~scanf ("%d" , &num)){ sum += num; cout << sum <<endl ; } return 0 ; }
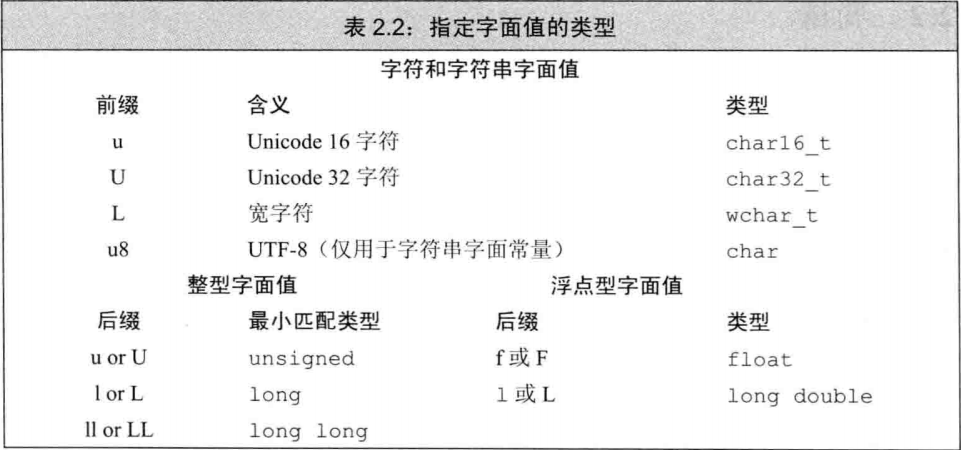
第二章 2.1 C++ guarantees short and int is at least 16 bits, long at least 32 bits, long long at least 64 bits.
2.2 use double, or also float.
2.3 & 2.4 在表达式内如果有了无符号数,最后是一个负值,那么编译器会取模。
2.5 ~ 2.7
十进制:20 & 八进制:020 & 十六进制:0x20或者0X20
2.8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;int main () cout << "2M" << '\n' ; cout << '2' << '\t' << 'M' << '\n' ; return 0 ; }
2.9 先定义 & 3.14被强转为3 & wage未定义 & 同2
2.10 glo_str = “” & glo_int = 0 & loc_int 不确定 & loc_str = “”
2.11 定义 & 定义 & 声明
2.12 字母+数字+下划线(必须以字母或者下划线开头)
C++中关于变量命名的规范:
能体现变量的实际意义 变量名一般采用小写字母 用户自定义类名一般以大写字母开头 多个单词定义的变量名应有区分Student_loan 而不是 Studentloan
错,double 是关键字 & 对 & 不能带- & 不能数字开头 & 对
2.13 j = 100,因为在这个语句块内,局部变量 i(100) 生效,如果想用全局变量 i(42) ,可以使用 j = ::i;
2.14 i = 100, sum=45, for循环语句内的i只活在该语句内,而 std::cout 在main语句块内,自然是取得100
2.15 可以 & 不行,引用需绑定对象 & 可以 & 不行,引用必须初始化
2.16 隐式类型转换
2.17 10 10,等于给 i = 5 后 i = 10
2.18 1 2 3 int a = 1 , b =2 , *p = a;*p = 10 ; p = &b;
2.19 指针自己本身就是一个对象,指针之间可以相互赋值和拷贝,在其生命周期内还可指向不同的对象 & 引用在汇编代码中就是指针常量
指针无需在定义时初始化 & 引用必须初始化
指针需要解引用 & 引用不需要
2.20 42的平方
2.21 非法,类型不一 & 非法,无取地址符号 & 合法
2.22 如果指针不是空&如果指针指向的对象的值不是0
2.24 因为 long 与 int 类型不匹配,而 void 指针可以接收任意类型的指针
因为 void 指针只知道头地址,它并不需要该对象的长度
2.25 int 指针 ip,int 变量 i,int 引用 r 绑定 i & int 变量 i,int 指针 p 为空 & ip 指针,ip2 变量
2.26 错,没有初始化 & 对 & 对 & ++sz 错误,常量不更改
2.27 错,引用需要绑定对象 & 如果 i2 不是 const 就对 & 同1 & 对 & 对 & 错,没有引用的 const,引用不是对象 & 对
2.28 指针常量需初始化 & 同1 & 常量 ic 需初始化 & 同1 & 对
2.29 对 & const int 和 int 不对等 & 同上 & 错,指针常量不能更改其值 & 同上 & 常量不能改变
2.30 顶层 & 底层 & 顶层 & 底层
2.31 对 & 错,底层 const & 对 & 同2 & 对
2.32 *p = nullptr;
2.33 & 2.34 对 & 对 & 对 & d 是整数指针 *d 就行 & 错,解引用也不行,指向的是常量 & g 是引用,ci 是常量
2.35 int & const int 引用 & const int 指针 & const int & 同2
2.36 & 2.37 c int & d int 引用
2.38 decltype 处理顶层 const 和引用的方式与 auto 有些许不同。
decltype((var)) 的结果永远是引用。
如果使用的表达式是个变量,则 decltype 返回该变量的类型。
(包括顶层 const 和引用在内)
而 auto 会忽略顶层 const,以及直接识别引用绑定的对象。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 int i = 0 , &r = i;auto a = i;decltype (i) b = i;auto c = r;decltype (r) d = i;
2.39 1 2 3 4 D:\WorkSpace\C++\Test.cpp:5 :2 : 错误:结构定义后需要‘;’ } int main () ^ ;
第三章 3.1 头文件中不应使用using声明,以避免名字冲突
3.2 1 2 3 string s;getline(cin ,s); while (cin >> s);
3.3 对于 string 类的输入函数,它会自动忽略开头的空白(空格、制表符、换行等等),从第一个真正的字符开始直到下一个空白。
对于 getline() 函数,它会保存字符串中的空白符,它读入数据,直到遇到换行符位置。
3.4 1 2 3 cin >> s1 >> s2;cout << (s1 > s2 ? s1 : s2) << endl ;cout << (s1.size() > s2.size() ? s1 : s2) << endl ;
3.5 1 2 3 cin >> s1 >> s2;cout << s1 + s2;cout << s1 + " " + s2 << endl ;
3.6 1 2 3 for (auto &c : s){ C = 'X' ; }
3.7 没有改变,因为变量只是 char 而不是 char 引用
3.8 1 2 3 4 5 6 while (i < s.size()){ s[i++]='X' ; } for (int i = 0 ;i < s.size();i++){ s[i++]='X' ; }
范围for,写起来快
3.9 不合法,越界了,或许确实可以输出一个空格,但是不要这么做
3.10 1 2 3 4 cin >> s;for (auto &c:s){ if (!ispunct (c))cout << c; }
3.11 const char&
3.12 vector的初始化:
1:引用不可以成为vector的元素,因为其不是对象。
2:可以用花括号初始化每一个值。
3:可以用括号指定元素个数或相同的元素值
对 & 不对,类型不一 & 对
3.13 0 & 10个0 & 10个42 & 10 & 10,42 & 10个“” & 10个“hi”
3.14 & 3.15 1 while (cin >> num) vec.push_back(num);
3.16 1 2 3 4 5 cout << s.size() << endl ;for (auto c:s){ cout << c << endl ; }
3.17 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 while (cin >> s){ vec.push_back(s); } for (auto c:s){ for (auto ch:c){ cout << toupper (ch); } cout << endl ; }
3.18 3.19 1 2 3 4 vector <int > vec(10 ,42 );vector <int > vec{42 ,..,42 };int a[]={42 ,...,42 };vector <int > vec(a,a+10 );
3.20 1 2 3 4 5 6 for (int i=0 ;i<vec.size()-1 ;i++){ cout << vec[i]+vec[i+1 ] << endl ; } for (int i=0 ;i<vec.size()/2 ;i++){ cout << vec[i]+vec[n-i-1 ] << endl ; }
3.21 1 2 3 4 5 cout << s.size() << endl ;for (auto c = s.cbegin();c != s.cend();c++){ cout << *c << endl ; }
3.22 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 vector <string > text;string s;while (getline(cin ,s)) text.push_back(s);for (auto it = text.begin();it != text.end();it++){ for (auto &c:*it) c=toupper (c); cout << *it <<endl ; }
3.23 1 2 3 4 5 vector <int > vec(10 ,2 );for (auto &c:vec){ c<<=1 ; cout << c << " " ; }
3.24 1 2 3 4 5 6 for (auto i=vec.begin();i!=end()-1 ;i++){ cout << *i+*(i+1 ) << endl ; } for (auto i=vec.begin(),j=vec.end();i!=j;i++,j--){ cout << *i + *j << endl ; }
3.25 1 2 3 for (auto c=vec.begin();c!=vec.end();c++){ sc[*c/10 ]++; }
3.26 因为vector迭代器并无加法运算符
3.27 对 & 对 & 如果txt_size()函数是constexpr修饰的就可 & 错,‘\0’放不下了
3.28 十个“” & 十个0 & 十个“” & 十个随机值
3.29
数组初始化必须知道大小
vector内置函数支持
vector自动扩容
3.30 3.31 1 2 3 4 int num[10 ];for (int i=0 ;i<10 ;i++){ num[i]=i; }
3.32 1 vector <int > vec(num,num+10 );
3.33 初始值未知,则最终的累加结果并无意义
3.34 相当于p1=p2
3.35 1 for (int *p=begin(num);p != end(num);p++) *p=0 ;
3.36 1 2 for (int *p=begin(num1),*q=begin(num2);p != end(num1)&&q != end(num2);p++,q++) if (*p!=*q) return false ;for (auto p=num1.begin(),q=num2.end();p != num1.end()&&q != num2.end();p++,q++) if (*p!=*q) return false ;
3.37 hello,按字节输出
3.38 两个地址相加得到的地址没什么实际意义,除非是目标地址就是这两个地址相加才能得到的,但这实在是没啥意义。
3.39 1 2 if (s1==s2);auto ans = strcmp (s1,s2);
3.40 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 const char s1[] = "Hello" ;const char s2[] = "world!" ; size_t n = strlen (s1) + strlen (" " ) + strlen (s2) + 1 ;char * s3 = new char [n]; strcpy (s3, s1);strcat (s3, " " );strcat (s3, s2);
3.41 1 vector <int > vec(num,num+10 );
3.42 1 for (int i=0 ;i<vec.size();i++) num[i] = vec[i];
3.43 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 int ia[3 ][4 ] = {0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 };for (const int (&p)[4 ] : ia) for (int q : p) cout << q << " " ; cout << endl ;for (size_t i = 0 ; i != 3 ; ++i) for (size_t j = 0 ; j != 4 ; ++j) cout << ia[i][j] << " " ; cout << endl ;for (int (*p)[4 ] = ia; p != ia + 3 ; ++p) for (int * q = *p; q != *p + 4 ; ++q) cout << *q << " " ;
3.44 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 using int_array = int [4 ];for (int_array& p : ia) for (int q : p) cout << q << " " ; cout << endl ;for (int_array* p = ia; p != ia + 3 ; ++p) for (int * q = *p; q != *p + 4 ; ++q) cout << *q << " " ;
3.45 1 2 3 4 5 6 for (auto & p : ia) for (int q : p) cout << q << " " ; cout << endl ;for (auto * p = ia; p != ia + 3 ; ++p) for (int * q = *p; q != *p + 4 ; ++q) cout << *q << " " ;
第四章 4.1 105
4.2 (vec.begin()) & (vec.begin())+1
4.3 可以,编写者自己用括号强制约定就行,可读性也强
4.4 ((12 / 3) 4) + (5 15) +((24 % 4) / 2) = 91
4.5 -86 & -18 & 0 & -2
4.6 1 2 if (num % 2 == 0 );if (num ^ 1 == 0 );
4.7 1 2 3 short a = 32768 ;unsigned a = -10 ;int a = 123456789 *123456789 ;
4.8 逻辑与:左面为真再判断右面
逻辑或:先判断左面为假再判断右面
相等性运算符:右边的转换为左边的类型再与左边比较
4.9 先看cp是否是空指针,随后看cp所指向的地方是否为空
4.10 1 while (cin >> num && num != 42 );
4.11 1 if (a>b?(b>c?(c>d?true :false ):false ):false );
4.12 判断i是否为相应时刻(j<k)的0或者1
4.13 3.0 & 3 & 3 & 3.5
4.14 右值不可放在表达式左侧 & 恒为true
4.15 非法,得先让pi指向某个int类型的左值,然后把表达式改为dval = ival = *pi = 0即可。
4.16 !=优先级高于=,(p = getPtr()) != 0 & 恒为true,if(i == 1024)
4.17 前置返回i+1,后置返回i然后再+1
4.18 第一个没有输出,并且还会输出v.end()
4.19 指针不为空且指针里不为空并往下一步走 & 后两个改成ival+1
4.20 解引用后迭代器+1 & 迭代器里的是string无法自增 & 不合法,iter无法使用点运算符 & iter指向的是否为空 & string无自增 & iter指向是否为空,然后迭代器加一
4.21 1 for (auto &c:vec) c % 2 ? c *= 2 : c;
4.22 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 string Sscore = score < 60 ? "fail" : (score < 75 ? "low pass" : (score < 90 ? "pass" : "high pass" ));if (score<60 ) Sscore = "fail" ;else if (score<75 ) Sscore = "low pass" ;else if (score<90 ) Sscore = "pass" ;else Sscore = "high pass" ;
4.23 1 2 string s = "word" ;string p1 = s + (s[s.size() - 1 ] == 's' ? "" : "s" );
4.24 Since we are nesting conditional operations, we are essentially grouping expressions with each others using operators of equal precedence, i.e., two ?: operators. Here, the rules of associativity dictates how the expressions of these operators are grouped together and eventually evaluated. Right associativity means that they will be grouped from right to left as such:
1 finalgrade = (grade > 90 ) ? "high pass" : ((grade < 60 ) ? "fail" : "pass" );
Note how this grouping means that outer conditional operation will not be evaluated until the inner one is evaluated first, if the grade is less than or equal to 90.
If the operator were left associative we would have the following grouping instead:
1 finalgrade = ((grade > 90 ) ? "high pass" : (grade < 60 )) ? "fail" : "pass" ;
This would result in a compile error because the outer conditional operator would have incompatible operand types: const char * and bool.
4.25 -7296
4.26 The C++ standard does not specify the size of integral types in bytes, but it specifies minimum ranges they must be able to hold. The minimum range of unsigned int is 0 to 65535. Since some implementations use only the minimum 16 bits for unsigned int, this could cause undefined behavior.
4.27 1 2 unsigned long ull = 3 , ul2 = 7 ;0101 & 0111 & true & false
4.28 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 using std ::cout ;using std ::endl ; cout << "void: nullptr_t\t" << sizeof (std ::nullptr_t ) << " bytes" << endl << endl ; cout << "bool:\t\t" << sizeof (bool ) << " bytes" << endl << endl ; cout << "char:\t\t" << sizeof (char ) << " bytes" << endl ;cout << "wchar_t:\t" << sizeof (wchar_t ) << " bytes" << endl ;cout << "char16_t:\t" << sizeof (char16_t ) << " bytes" << endl ;cout << "char32_t:\t" << sizeof (char32_t ) << " bytes" << endl << endl ; cout << "short:\t\t" << sizeof (short ) << " bytes" << endl ;cout << "int:\t\t" << sizeof (int ) << " bytes" << endl ;cout << "long:\t\t" << sizeof (long ) << " bytes" << endl ;cout << "long long:\t" << sizeof (long long ) << " bytes" << endl << endl ; cout << "float:\t\t" << sizeof (float ) << " bytes" << endl ;cout << "double:\t\t" << sizeof (double ) << " bytes" << endl ;cout << "long double:\t" << sizeof (long double ) << " bytes" << endl << endl ;cout << "int8_t:\t\t" << sizeof (int8_t ) << " bytes" << endl ;cout << "uint8_t:\t" << sizeof (uint8_t ) << " bytes" << endl ;cout << "int16_t:\t" << sizeof (int16_t ) << " bytes" << endl ;cout << "uint16_t:\t" << sizeof (uint16_t ) << " bytes" << endl ;cout << "int32_t:\t" << sizeof (int32_t ) << " bytes" << endl ;cout << "uint32_t:\t" << sizeof (uint32_t ) << " bytes" << endl ;cout << "int64_t:\t" << sizeof (int64_t ) << " bytes" << endl ;cout << "uint64_t:\t" << sizeof (uint64_t ) << " bytes" << endl ;
4.29 1 2 3 int x[10 ]; int *p = x;cout << sizeof (x)/sizeof (*x) << endl ;cout << sizeof (p)/sizeof (*p) << endl ;
4.30 1 2 3 4 sizeof x + y sizeof p->mem[i] sizeof a < b sizeof f ()
4.31 Advice: Use Postfix Operators only When Necessary
Readers from a C background might be surprised that we use the prefix increment in the programs we’ve written. The reason is simple: The prefix version avoids unnecessary work. It increments the value and returns the incremented version.The postfix operator must store the original value so that it can return the unincremented value as its result. If we don’t need the unincremented value, there’s no need for the extra work done by the postfix operator.
For ints and pointers, the compiler can optimize away this extra work. For more complicated iterator types, this extra work potentially might be more costly. By habitually using the prefix versions, we do not have to worry about whether the performance difference matters. Moreover—and perhaps more importantly—we can express the intent of our programs more directly.
4.32 1 2 3 4 5 6 constexpr int size = 5 ;int ia[size] = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 };for (int *ptr = ia, ix = 0 ; ix != size && ptr != ia+size; ++ix, ++ptr) { }
4.33 1 2 someValue ? ++x, ++y : --x, --y
4.34 1 2 3 if (fval);dval = fval + ival; dval + ival * cval;
4.35 1 2 3 4 cval = 'a' + 3 ; fval = ui - ival * 1.0 ; dval = ui * fval; cval = ival + fval + dval;
4.36 4.37 1 2 3 4 5 int i;double d;const string *ps;char *pc;void *pv;pv = (void *)ps; i = int (*pc); pv = &d; pc = (char *) pv;
4.38 1 double slope = static_cast <double >(j/i);
第五章 5.1 To be used as spaceholder
5.2 块是用花括号括起来的(可能为空的)语句和声明的序列 & 如果在程序的某个地方,语法上需要一条语句,但是逻辑上需要多条语句,那就用块
5.3 1 2 while (val <= 10 ) sum+=val,++val;
5.4 1 2 3 4 5 6 string ::iterator iter;while (iter != s.end()){}bool status;while (status = find(word)){}if (!status){}
5.5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 vector <int > stu{50 , 60 , 20 , 100 };vector <string > sc{"F" , "E" , "D" , "C" , "B" , "A" };for (auto c : stu){ if (c < 60 ) cout << sc[0 ] << endl ; cout << sc[(c - 50 ) / 10 ] << endl ; }
5.6 1 c < 60 ? sc[0 ] : sc[(c-50 )/10 ];
5.7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 if (ival1 != ival2) ival1 = ival2; else ival1 = ival2 = 0 ;if (ival < minval){ minval = ival; occurs = 1 ; } int ival;if (ival=get_value()) cout << "ival= " << ival << endl ; else cout << "ival = 0\n" ;if (ival = 0 ) ival = get_value();
5.8 if 比 else 多的时候, else 会与最近的 if 配套
5.9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 unsigned aCnt = 0 , eCnt = 0 , iCnt = 0 , oCnt = 0 , uCnt = 0 ;char ch;while (cin >> ch){ if (ch == 'a' ) ++aCnt; else if (ch == 'e' ) ++eCnt; else if (ch == 'i' ) ++iCnt; else if (ch == 'o' ) ++oCnt; else if (ch == 'u' ) ++uCnt; }
5.10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 while (cin >> ch) switch (ch) { case 'a' : case 'A' : ++aCnt; break ; case 'e' : case 'E' : ++eCnt; break ; case 'i' : case 'I' : ++iCnt; break ; case 'o' : case 'O' : ++oCnt; break ; case 'u' : case 'U' : ++uCnt; break ; }
5.11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 while (cin >> std ::noskipws >> ch) switch (ch) { case 'a' : case 'A' : ++aCnt; break ; case 'e' : case 'E' : ++eCnt; break ; case 'i' : case 'I' : ++iCnt; break ; case 'o' : case 'O' : ++oCnt; break ; case 'u' : case 'U' : ++uCnt; break ; case ' ' : ++spaceCnt; break ; case '\t' : ++tabCnt; break ; case '\n' : ++newLineCnt; break ; }
5.12 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 while (cin >> std ::noskipws >> ch){ switch (ch) { case 'a' : case 'A' : ++aCnt; break ; case 'e' : case 'E' : ++eCnt; break ; case 'i' : if (prech == 'f' ) ++fiCnt; case 'I' : ++iCnt; break ; case 'o' : case 'O' : ++oCnt; break ; case 'u' : case 'U' : ++uCnt; break ; case ' ' : ++spaceCnt; break ; case '\t' : ++tabCnt; break ; case '\n' : ++newLineCnt; break ; case 'f' : if (prech == 'f' ) ++ffCnt; break ; case 'l' : if (prech == 'f' ) ++flCnt; break ; } prech = ch; }
5.13 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 unsigned aCnt = 0 , eCnt = 0 , iouCnt = 0 ;char ch = next_text();switch (ch) { case 'a' : aCnt++; case 'e' : eCnt++; default : iouCnt++; } unsigned index = some_value();int ix;switch (index) { case 1 : ix = get_value(); ivec[ ix ] = index; break ; default : ix = ivec.size()-1 ; ivec[ ix ] = index; } unsigned evenCnt = 0 , oddCnt = 0 ;int digit = get_num() % 10 ;switch (digit) { case 1 , 3 , 5 , 7 , 9 : oddcnt++; break ; case 2 , 4 , 6 , 8 , 10 : evencnt++; break ; } const unsigned ival=512 , jval=1024 , kval=4096 ;unsigned bufsize;unsigned swt = get_bufCnt();switch (swt) { case ival: bufsize = ival * sizeof (int ); break ; case jval: bufsize = jval * sizeof (int ); break ; case kval: bufsize = kval * sizeof (int ); break ; }
5.14 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 pair<string , int > max_duplicated; int count = 0 ;for (string str, prestr; cin >> str; prestr = str){ if (str == prestr) ++count; else count = 0 ; if (count > max_duplicated.second) max_duplicated = {prestr, count}; } if (max_duplicated.first.empty()) cout << "There's no duplicated string." << endl ; else cout << "the word " << max_duplicated.first << " occurred " << max_duplicated.second + 1 << " times. " << endl ;
5.15 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 int ix;for (ix = 0 ; ix != sz; ++ix){}if (ix != sz);int ix;for (; ix != sz; ++ix){}for (int ix = 0 ; ix != sz; ++ix){}
5.16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 int i;while (cin >> i);for (int i = 0 ; cin >> i;);for (int i = 0 ; i != size; ++i);int i = 0 ;while (i != size) ++i;
5.17 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 bool is_pre (vector <int > &l, vector <int > &r) if (l.size()>r.size()) return is_pre(r,l); for (int i=0 ;i<l.size();i++){ if (l[i]!=r[i]) return false ; } return true ; } int main () vector <int > l{0 ,1 ,1 ,2 }; vector <int > r{0 ,1 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,5 ,8 }; cout << (is_pre(l,r) ? "Yes" : "No" ); return 0 ; }
5.18 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 do { int v1, v2; cout << "Please enter two numbers to sum:" ; if (cin >> v1 >> v2) cout << "Sum is: " << v1 + v2 << endl ; }while (cin ); do { }while (ival = get_response()); int ival = get_response();do { ival = get_response(); }while (ival);
5.19 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 string s1,s2;do { cout << "Please input two string:\n" ; cin >> s1 >> s2; cout << (s1.size() > s2.size() ? s2 : s1) << endl ; cout << "Do you wanna continue?(yes or no)\n" ; cin >> s1; }while (!s1.empty() && tolower (s1[0 ]=='y' ));
5.20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 string re,t;while (cin >> re) if (re == t) break ; else t=re; if (cin .eof()) cout << "No repeated" << endl ; else cout << re << endl ;
5.21 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 string curr, prev;bool no_twice = true ;while (cin >> curr) { if (isupper (curr[0 ]) && prev == curr) { cout << curr << endl ; no_twice = false ; break ; } prev = curr; } if (no_twice) cout << "no word was repeated." << endl ;
5.22 1 for (int sz = get_size(); sz <= 0 ; sz = get_size());
5.23 ~ 5.25 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 cin >> i >> j;cout << i / j <<endl ;if (j == 0 ) throw runtime_error("divisor is 0" ); cout << i / j << endl ;for (int i, j; cout << "Input two integers:\n" , cin >> i >> j; ){ try { if (j == 0 ) throw runtime_error("divisor is 0" ); cout << i / j << endl ; } catch (runtime_error err) { cout << err.what() << "\nTry again? Enter y or n" << endl ; char c; cin >> c; if (!cin || c == 'n' ) break ; } }
第六章 6.1 形参:在函数参数表中声明的局部变量,它们由函数调用中提供的实参初始化
实参:函数调用中提供的用于初始化函数形参的值
6.2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 int f () string s; return s; } void f2 (int i) int calc (int v1,int v2) double square (double x) return x * x; }
6.3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 int fact (int i) if (i < 0 ){ runtime_error err ("Input cannot be a negative number" ) ; cout << err.what() << endl ; } return i > 1 ? i * fact(i-1 ) : i; }
6.4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 int main () int n; cout << "Please input a number\n" ; cin >> n; cout << fact(n) << endl ; return 0 ; }
6.5 1 2 3 4 5 int myAbs (int i) if (i < 0 ) return -i; return i; }
6.6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 size_t count_add(int n){ static size_t ctr = 0 ; ctr += n; return ctr; } int main () for (size_t i = 0 ; i != 10 ; ++i) cout << count_add(i) << endl ; return 0 ; }
6.7 1 2 3 4 5 size_t count_add(int n){ static size_t ctr = 0 ; return ctr++; }
6.8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 #pragma once int fact (int val) int func () template <typename T> T abs (T i) return i >= 0 ? i : -i; }
6.9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 #include "Chapter6.h" #include <iostream> int fact (int val) if (val == 0 || val == 1 ) return 1 ; else return val * fact(val-1 ); } int func () int n, ret = 1 ; std ::cout << "input a number: " ; std ::cin >> n; while (n > 1 ) ret *= n--; return ret; } #include "Chapter6.h" #include <iostream> int main () std ::cout << "5! is " << fact(5 ) << std ::endl ; std ::cout << func() << std ::endl ; std ::cout << abs (-9.78 ) << std ::endl ; return 0 ; }
6.10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 void swap (int *p,int *q) int t = *p; *p = *q; *q = t; } int main () int i,j; cin >> i >> j; swap(&i,&j); cout << i << j; return 0 ; }
6.11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 void reset (int &i) i = 0 ; } int main () int i = 1 ; reset(i); cout << i << endl ; return 0 ; }
6.12 1 2 3 4 5 6 void swap (int &l,int &r) int t = l; l = r; r = t; }
6.13 6.14 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 void reset (int &i) i = 0 ; } void print (std ::vector <int >::iterator begin, std ::vector <int >::iterator end) for (std ::vector <int >::iterator iter = begin; iter != end; ++iter) std ::cout << *iter << std ::endl ; }
6.15 函数不修改 s 的值,但是 occurs 的值是会变化的 & 因为 c 可能是个临时变量 & 那 s 就可能被改变 & 无法改变 occurs 的值,occurs = 0 就会报错
6.16 1 2 3 bool is_empty (const string & s) return s.empty(); }
6.17 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 bool hav_up (const string & s) for (auto c:s){ if (isupper (c))return true ; } return false ; } void toUpperString (string & s) for (auto & c:s){ c = toupper (c); } }
6.18 1 2 3 bool compare (matrix &a,matrix &b) vector <int >::iterator change_val (int a,vector <int >::iterator b) ;
6.19 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 double calc (double ) int count (const string &,char ) int sum (vector <int >::iterator,vector <int >::iterator,int ) vector <int > vec(10 );calc(23.4 ,55.1 ); count("abcda" ,'a' ); calc(66 ); sum(vec.begin(),vec.end(),3.8 );
6.20 If we can use const, just use it. If we make a parameter a plain reference when it could be a reference to const, the reference value maybe changed.
6.21 1 2 3 int com (int a,const int *const b) return a > *b ? a : *b; }
6.22 1 2 3 4 5 void swap (int *& p,int *& q) auto t = p; p = q; q = t; }
6.23 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 void print (const int * p) if (p) cout << *p << endl ; } void print (const char * p) if (p) while (*p) cout << *p++; cout << endl ; } void print (const int * beg,const int * end) while (beg != end) cout << *beg++ <<endl ; } void print (const int a[],size_t size) for (size_t i = 0 ;i < size;i++) cout << a[i] << endl ; } void print (int (&arr)[2 ]) for (auto i:arr) cout << i << endl ; } int main () int i = 0 , j[2 ] = {0 , 1 }; char ch[5 ] = "test" ; print(&i); print(ch); print(begin(j),end(j)); print(j,end(j)-begin(j)); print(j); return 0 ; }
6.24 1 2 3 4 void print (const int (&a)[10 ]) for (size_t i = 0 ;i != 10 ;++i) cout << a[i] << endl ; }
6.25 & 6.26 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 #include <iostream> #include <string> int main (int argc, char **argv) std ::string str; for (int i = 1 ; i != argc; ++i) str += std ::string (argv[i]) + " " ; std ::cout << str << std ::endl ; return 0 ; }
6.27 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 #include <iostream> #include <initialzer_list> using namespace std ;int sum (initialzer_list<int > const & il) int sum = 0 ; for (auto i:il) sum += i; return sum; } int main () auto il = {1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 }; cout << sum(il) << endl ; return 0 ; }
6.28 const string&
6.29 Depends on the type of elements of initializer_list. When the type is PODType , reference is unnecessary. Because POD is cheap to copy (such as int). Otherwise, Using reference(const) is the better choice.
6.30 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 bool str_subrange (const string &str1, const string &str2) if (str1.size() == str2.size()) return str1 == str2; auto size = (str1.size() < str2.size()) ? str1.size() : str2.size(); for (decltype (size) i = 0 ; i != size; ++i){ if (str1[i] != str2[i]) return ; } }
6.31 It is valid to return a reference when the reference does not refer to a local object. The Same applies for a reference to const, but only when the returned value is not expected to be an lvalue.
6.32 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 int &get (int *arry, int index) return arry[index];}int main () int ia[10 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i != 10 ; ++i) get(ia, i) = i; return 0 ; }
6.33 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 using Iter = vector <int >::const_iterator;void print (Iter first, Iter last) if (first != last) { cout << *first << " " ; print(++first, last); } }
6.34 When the recursion termination condition becomes var != 0, two situations can happen :
case 1 : If the argument is positive, recursion stops at 0.(Note : There is one extra multiplication step though as the combined expression for factorial(5) reads 5 4 3 2 1 * 1. In terms of programming languages learning, such subtle difference probably looks quite trivial. In algorithms analysis and proof, however, this extra step may be super important.)
case 2 : if the argument is negative, recursion would never stop. As a result, a stack overflow would occur.
6.35 val-- 的值是 val , 陷入死循环
6.36 & 6.37 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 string (&fun(string (&arr)[10 ]))[10 ];typedef string [10 ] strarr;using strarr = string [10 ];strarr &fun (strarr& arr) ;auto fun(strarr& arr) -> string(&)[10]; string [10 ] sarr;decltype (sarr) &fun(strarr& arr);
6.38 1 2 3 4 5 int odd[] = {1 ,3 ,5 ,7 ,9 };int even[] = {0 ,2 ,4 ,6 ,8 };decltype (odd) &arrPtr(int i){ return (i % 2 ) ? &odd : &even; }
6.39 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 int calc (int , int ) int calc (const int , const int ) int get () double get () int *reset (int *) double *reset (double *)
6.40 1 2 int ff (int a, int b = 0 , int c = 0 ) char *init (int ht = 24 ,int wd, char bckgrnd)
6.41 1 2 3 4 char *init (int ht, int wd = 80 , char bckgrnd = ' ' ) init(); init(24 ,10 ); init(14 ,'*' );
6.42 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 string make_plural (size_t ctr, const string &word, const string &ending = "s" ) return (ctr > 1 ) ? word + ending : word; } int main () cout << "singual: " << make_plural(1 , "success" , "es" ) << " " << make_plural(1 , "failure" ) << endl ; cout << "plural : " << make_plural(2 , "success" , "es" ) << " " << make_plural(2 , "failure" ) << endl ; return 0 ; }
6.43 Both two should put in a header. (a) is an inline function. (b) is the declaration of useful function. we always put them in the header.
6.44 1 2 3 4 inline bool is_shorter (const string &lft, const string &rht) return lft.size() < rht.size(); }
6.45 For example, the function arrPtr in Exercise 6.38 and make_plural in Exercise 6.42 should be defined as inline. But the function func in Exercise 6.4 shouldn’t. It is not that small and it’s only being called once. Hence, it will probably not expand as inline.
6.46 (Two explanations) No. Because std::string::size() is not a constexpr function and s1.size() == s2.size() is not a constant expression.
For a non-template, non-defaulted constexpr function or a non-template, non-defaulted, non-inheriting constexpr constructor, if no argument values exist such that an invocation of the function or constructor could be an evaluated subexpression of a core constant expression (5.19), the program is ill-formed; no diagnostic required. (N3690 §7.1.5 [dcl.constexpr]/5)
显然 isShorter 函数不符合 constexpr 函数的要求,它虽然只有一条 return 语句,但是返回的结果调用了标准库 string 类的 size() 函数和 < 比较符,无法构成常量表达式,因此不能改写成 constexpr 函数。
constexpr 函数是指能用于常量表达式的函数,constexpr函数的返回类型和所有形参的类型都得是字面值类型,而且函数体中必须有且只有一条 return语句。
6.47 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 void printVec (vector <int > &vec) #ifndef NDEBUG cout << "vector size: " << vec.size() << endl ; #endif if (!vec.empty()) { auto tmp = vec.back(); vec.pop_back(); printVec(vec); cout << tmp << " " ; } } int main () vector <int > vec{ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 }; printVec(vec); cout << endl ; return 0 ; }
6.48 1 2 3 string s;while (cin >> s && s != sought){}assert(s == sought);
6.49 candidate function:
Set of functions that are considered when resolving a function call. (all the functions with the name used in the call for which a declaration is in scope at the time of the call.)
viable function:
Subset of the candidate functions that could match a given call. It have the same number of parameters as arguments to the call, and each argument type can be converted to the corresponding parameter type.
6.50 1 2 3 4 f(2.56 , 42 ); f(42 ); f(42 , 0 ); f(2.56 , 3.14 );
6.51 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 void f () cout << "f()" << endl ; } void f (int ) cout << "f(int)" << endl ; } void f (int , int ) cout << "f(int, int)" << endl ; } void f (double , double ) cout << "f(double, double)" << endl ; } int main () f(42 ); f(42 , 0 ); f(2.56 , 3.14 ); return 0 ; }
6.52 1 2 3 void manip (int , int ) manip('a' , 'z' ); manip(55.4 , dobj);
6.53 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 int calc (int &, int &) int calc (const int &, const int &) int calc (char *, char *) int calc (const char *, const char *) int calc (char *, char *) int calc (char * const , char * const )
6.54 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 int func (int a, int b) using pFunc1 = decltype (func) *;typedef decltype (func) *pFunc2using pFunc3 = int (*)(int a, int b);using pFunc4 = int (int a, int b);typedef int (*pFunc5) (int a, int b) using pFunc6 = decltype (func);std ::vector <pFunc1> vec1;std ::vector <pFunc2> vec2;std ::vector <pFunc3> vec3;std ::vector <pFunc4*> vec4;std ::vector <pFunc5> vec5;std ::vector <pFunc6*> vec6;
6.55 1 2 3 4 int add (int a, int b) return a + b; }int subtract (int a, int b) return a - b; }int multiply (int a, int b) return a * b; }int divide (int a, int b) return b != 0 ? a / b : 0 ; }
6.56 1 2 3 std ::vector <decltype (func) *> vec{ add, subtract, multiply, divide };for (auto f : vec) std ::cout << f(2 , 2 ) << std ::endl ;
第七章 7.1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 struct Sales_data { string bookNo; unsigned units_sold = 0 ; double revenue = 0.0 ; }; int main () Sales_data total; if (cin >> total.bookNo >> total.units_sold >> total.revenue) { Sales_data trans; while (cin >> trans.bookNo >> trans.units_sold >> trans.revenue) { if (total.bookNo == trans.bookNo) { total.units_sold += trans.units_sold; total.revenue += trans.revenue; } else { cout << total.bookNo << " " << total.units_sold << " " << total.revenue << endl ; total = trans; } } cout << total.bookNo << " " << total.units_sold << " " << total.revenue << endl ; } else { std ::cerr << "No data?!" << std ::endl ; return -1 ; } return 0 ; }
7.2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 struct Sales_data { string isbn () return bookNo;} Sales_data& combine (const Sales_data &rhs) ; string bookNo; unsigned units_sold = 0 ; double revenue = 0.0 ; }; Sales_data& Sales_data::combine(const Sales_data &rhs){ units_sold += rhs.units_sold; revenue += rhs.revenue; return *this ; }
7.3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 int main () Sales_data total; if (cin >> total.bookNo >> total.units_sold >> total.revenue) { Sales_data trans; while (cin >> trans.bookNo >> trans.units_sold >> trans.revenue) { if (total.isbn() == trans.isbn()) { total.combine(trans); } else { cout << total.bookNo << " " << total.units_sold << " " << total.revenue << endl ; total = trans; } } cout << total.bookNo << " " << total.units_sold << " " << total.revenue << endl ; } else { std ::cerr << "No data?!" << std ::endl ; return -1 ; } return 0 ; }
7.4 1 2 3 4 class Person { string name; string address; };
7.5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 class Person { string name; string address; public : auto getName () return name;} auto getAddress () return address;} };
7.6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 struct Sales_data { std ::string const & isbn () const return bookNo; }; Sales_data& combine (const Sales_data&) ; std ::string bookNo; unsigned units_sold = 0 ; double revenue = 0.0 ; }; Sales_data& Sales_data::combine(const Sales_data& rhs) { units_sold += rhs.units_sold; revenue += rhs.revenue; return *this ; } std ::istream &read (std ::istream &is, Sales_data &item) double price = 0 ; is >> item.bookNo >> item.units_sold >> price; item.revenue = price * item.units_sold; return is; } std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &os, const Sales_data &item) os << item.isbn() << " " << item.units_sold << " " << item.revenue; return os; } Sales_data add (const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs) Sales_data sum = lhs; sum.combine(rhs); return sum; }
7.7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 int main () Sales_data total; if (read(std ::cin , total)) { Sales_data trans; while (read(std ::cin , trans)) { if (total.isbn() == trans.isbn()) total.combine(trans); else { print(std ::cout , total) << std ::endl ; total = trans; } } print(std ::cout , total) << std ::endl ; } else { std ::cerr << "No data?!" << std ::endl ; return -1 ; } return 0 ; }
7.8 Define read‘s Sales_data parameter as plain reference since it’s intended to change the revenue‘s value.
Define print‘s Sales_data parameter as a reference to const since it isn’t intended to change any member’s value of this object.
7.9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Person { string name; string address; public : auto getName () return name;} auto getAddress () return address;} }; istream& read (istream& is, Person& a) { is >> a.name >> a.address; return is; } ostream& print (ostream& os, Person& a) { os << a.name << " " << a.address; return os; }
7.10 1 if (read(read(cin , data1), data2))
we can try to divide it like that:
1 2 3 std ::istream &firstStep = read(cin , data1);sdt::istream &secondStep = read(firstStep, data2); if (secondStep)
the condition of the if statement would read two Sales_data object at one time.
7.11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 #ifndef CP5_ex7_11_h #define CP5_ex7_11_h #include <string> #include <iostream> struct Sales_data { Sales_data() = default ; Sales_data(const std ::string &s):bookNo(s) { } Sales_data(const std ::string &s, unsigned n, double p):bookNo(s), units_sold(n), revenue(n*p){ } Sales_data(std ::istream &is); std ::string isbn () const return bookNo; }; Sales_data& combine (const Sales_data&) ; std ::string bookNo; unsigned units_sold = 0 ; double revenue = 0.0 ; }; std ::istream &read (std ::istream &is, Sales_data &item) double price = 0 ; is >> item.bookNo >> item.units_sold >> price; item.revenue = price * item.units_sold; return is; } std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &os, const Sales_data &item) os << item.isbn() << " " << item.units_sold << " " << item.revenue; return os; } Sales_data add (const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs) Sales_data sum = lhs; sum.combine(rhs); return sum; } Sales_data::Sales_data(std ::istream &is) { read(is, *this ); } Sales_data& Sales_data::combine(const Sales_data& rhs) { units_sold += rhs.units_sold; revenue += rhs.revenue; return *this ; } #endif #include "ex7_11.h" int main () Sales_data item1; print(std ::cout , item1) << std ::endl ; Sales_data item2 ("0-201-78345-X" ) ; print(std ::cout , item2) << std ::endl ; Sales_data item3 ("0-201-78345-X" , 3 , 20.00 ) ; print(std ::cout , item3) << std ::endl ; Sales_data item4 (std ::cin ) ; print(std ::cout , item4) << std ::endl ; return 0 ; }
7.12 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 struct Sales_data ;std ::istream &read (std ::istream&, Sales_data&) ;struct Sales_data { Sales_data() = default ; Sales_data(const std ::string &s):bookNo(s) { } Sales_data(const std ::string &s, unsigned n, double p):bookNo(s), units_sold(n), revenue(n*p){ } Sales_data(std ::istream &is) { read(is, *this ); } std ::string isbn () const return bookNo; }; Sales_data& combine (const Sales_data&) ; std ::string bookNo; unsigned units_sold = 0 ; double revenue = 0.0 ; }; Sales_data& Sales_data::combine(const Sales_data& rhs) { units_sold += rhs.units_sold; revenue += rhs.revenue; return *this ; } std ::istream &read (std ::istream &is, Sales_data &item) double price = 0 ; is >> item.bookNo >> item.units_sold >> price; item.revenue = price * item.units_sold; return is; }
7.13 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include "ex7_12.h" int main () Sales_data total (std ::cin ) ; if (!total.isbn().empty()) { std ::istream &is = std ::cin ; while (is) { Sales_data trans (is) ; if (!is) break ; if (total.isbn() == trans.isbn()) total.combine(trans); else { print(std ::cout , total) << std ::endl ; total = trans; } } print(std ::cout , total) << std ::endl ; } else { std ::cerr << "No data?!" << std ::endl ; return -1 ; } return 0 ; }
7.14 1 Sales_data() : bookNo("" ), units_sold(0 ) , revenue(0 ){}
7.15 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Person { string name; string address; public : Person() = default ; Person(const string s1,const string s2) : name(s1), address(s2){} Person(istream& is){ read(is, *this ); } auto getName () return name;} auto getAddress () return address;} }; istream& read (istream& is, Person& a) { is >> a.name >> a.address; return is; } ostream& print (ostream& os, Person& a) { os << a.name << " " << a.address; return os; }
7.16 没有限制 & 指定的访问级别将直到下一个访问控制符亦或结束 & 所有可以被访问的部分都应该在 public 说明符之后 & 所有不能被类外访问但可被类内访问的应在 private 之后
7.17 有,默认访问控制不同, class 是 private , struct 是 public
7.18 encapsulation is the separation of implementation from interface. It hides the implementation details of a type. (In C++, encapsulation is enforced by putting the implementation in the private part of a class)
Important advantages:
User code cannot inadvertently corrupt the state of an encapsulation object.
The implementation of an encapsulated class can change over time without requiring changes in user-level code.
7.19 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Person { string name; string address; public : Person() = default ; Person(const string s1,const string s2) : name(s1), address(s2){} Person(istream& is){ read(is, *this ); } auto getName () return name;} auto getAddress () return address;} }; istream& read (istream& is, Person& a) { is >> a.name >> a.address; return is; } ostream& print (ostream& os, Person& a) { os << a.name << " " << a.address; return os; }
7.20 friend is a mechanism by which a class grants access to its nonpublic members. They have the same rights as members.
Pros :
the useful functions can refer to class members in the class scope without needing to explicitly prefix them with the class name.
you can access all the nonpublic members conveniently.
sometimes, more readable to the users of class.
Cons :
lessens encapsulation and therefore maintainability.
code verbosity, declarations inside the class, outside the class.
7.21 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 class Sales_data {friend std ::istream &read (std ::istream &is, Sales_data &item) ;friend std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &os, const Sales_data &item) ;friend Sales_data add (const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs) public : Sales_data() = default ; Sales_data(const std ::string &s):bookNo(s) { } Sales_data(const std ::string &s, unsigned n, double p):bookNo(s), units_sold(n), revenue(n*p){ } Sales_data(std ::istream &is) { read(is, *this ); } std ::string isbn () const return bookNo; }; Sales_data& combine (const Sales_data&) ; private : std ::string bookNo; unsigned units_sold = 0 ; double revenue = 0.0 ; }; Sales_data& Sales_data::combine(const Sales_data& rhs) { units_sold += rhs.units_sold; revenue += rhs.revenue; return *this ; } std ::istream &read (std ::istream &is, Sales_data &item) double price = 0 ; is >> item.bookNo >> item.units_sold >> price; item.revenue = price * item.units_sold; return is; } std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &os, const Sales_data &item) os << item.isbn() << " " << item.units_sold << " " << item.revenue; return os; } Sales_data add (const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs) Sales_data sum = lhs; sum.combine(rhs); return sum; }
7.22 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Person {friend istream& read (istream& is, Person& a) friend ostream& print (ostream& os, Person& a) private : string name; string address; public : Person() = default ; Person(const string s1,const string s2) : name(s1), address(s2){} Person(istream& is){ read(is, *this ); } auto getName () return name;} auto getAddress () return address;} }; istream& read (istream& is, Person& a) { is >> a.name >> a.address; return is; } ostream& print (ostream& os, Person& a) { os << a.name << " " << a.address; return os; }
7.23 & 7.24 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Screen { public : using pos = string ::size_type; Screen() = defualt; Screen(pos ht, pos wd) : height(ht), width(wd), contents(ht * wd, ' ' ) {} Screen(pos ht, pos wd, char c) : height(ht), width(wd), contents(ht * wd, c) {} char get () return contents[cur]; } char get (pos r, pos c) return contents[r * width + c]; } private : pos cur = 0 ; pos height = 0 , width = 0 ; string contents; };
7.25 The class below can rely on it. It goes in Section 7.1.5 :
the synthesized versions are unlikely to work correctly for classes that allocate resources that reside outside the class objects themselves.
Moreover, the synthesized versions for copy, assignment, and destruction work correctly for classes that have vector or string members .
Hence the class below which used only built-in type and strings can rely on the default version of copy and assignment.
7.26 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 class Sales_data { friend std ::istream &read (std ::istream &is, Sales_data &item) ; friend std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &os, const Sales_data &item) ; friend Sales_data add (const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs) public : Sales_data() = default ; Sales_data(const std ::string &s) : bookNo(s) {} Sales_data(const std ::string &s, unsigned n, double p) : bookNo(s), units_sold(n), revenue(n * p) {} Sales_data(std ::istream &is) { read(is, *this ); } std ::string isbn () const return bookNo; }; Sales_data &combine (const Sales_data &) ; private : inline double avg_price () const private : std ::string bookNo; unsigned units_sold = 0 ; double revenue = 0.0 ; }; inline double avg_price () const return units_sold ? revenue / units_sold : 0 ; } Sales_data &Sales_data::combine(const Sales_data &rhs) { units_sold += rhs.units_sold; revenue += rhs.revenue; return *this ; } std ::istream &read (std ::istream &is, Sales_data &item) double price = 0 ; is >> item.bookNo >> item.units_sold >> price; item.revenue = price * item.units_sold; return is; } std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &os, const Sales_data &item) os << item.isbn() << " " << item.units_sold << " " << item.revenue; return os; } Sales_data add (const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs) Sales_data sum = lhs; sum.combine(rhs); return sum; }
7.27 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 class Screen { public : using pos = string ::size_type; Screen() = defualt; Screen(pos ht, pos wd) : height(ht), width(wd), contents(ht * wd, ' ' ) {} Screen(pos ht, pos wd, char c) : height(ht), width(wd), contents(ht * wd, c) {} char get () return contents[cur]; } char get (pos r, pos c) return contents[r * width + c]; } Screen &move (pos l, pos r) { cur = l * width + r; return *this ; } Screen &set (char c) { contents[cur] = c; return *this ; } Screen &set (pos l, pos r, char c) { contents[l * width + r] = c; return *this ; } Screen &display (ostream &os) { do_display(os); return *this ; } Screen &display (ostream &os) const { do_display(os); return *this ; } private : void do_display const (ostream &os) { os << contents; } private : pos cur = 0 ; pos height = 0 , width = 0 ; string contents; };
7.28 The second call to display couldn’t print # among the output, cause the call to set would change the temporary copy , not myScreen.
7.29 Yes
7.30 Pros
Cons
more to read
sometimes redundant
1 std ::string getAddr () const return this ->addr; }
7.31 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Y ;class X { Y* y = nullptr ; }; class Y { X x; };
7.32 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 class Screen ;class Window_mgr {public : using ScreenIndex = std ::vector <Screen>::size_type; inline void clear (ScreenIndex) private : std ::vector <Screen> screens; }; class Screen { friend void Window_mgr::clear(ScreenIndex); public : using pos = std ::string ::size_type; Screen() = default ; Screen(pos ht, pos wd):height(ht), width(wd), contents(ht*wd, ' ' ){ } Screen(pos ht, pos wd, char c):height(ht), width(wd), contents(ht*wd, c){ } char get () const return contents[cursor]; } char get (pos r, pos c) const return contents[r*width+c]; } inline Screen& move (pos r, pos c) inline Screen& set (char c) inline Screen& set (pos r, pos c, char ch) const Screen& display (std ::ostream &os) const return *this ; } Screen& display (std ::ostream &os) { do_display(os); return *this ; } private : void do_display (std ::ostream &os) const private : pos cursor = 0 ; pos height = 0 , width = 0 ; std ::string contents; }; inline void Window_mgr::clear(ScreenIndex i){ if (i >= screens.size()) return ; Screen &s = screens[i]; s.contents = std ::string (s.height * s.width, ' ' ); } inline Screen& Screen::move(pos r, pos c){ cursor = r*width + c; return *this ; } inline Screen& Screen::set (char c){ contents[cursor] = c; return *this ; } inline Screen& Screen::set (pos r, pos c, char ch){ contents[r*width+c] = ch; return *this ; }
7.33 1 2 3 4 Screen::pos Screen::size() const { return height * width; }
7.34 1 2 3 D:\WorkSpace\C++\A.cpp:8 :20 : 错误:‘pos’未声明 void dummy_fcn (pos height) ^~~
7.35 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 typedef string Type;Type initVal () ;class Exercise { public : typedef double Type; Type setVal (Type) ; Type initVal () ; private : int val; }; Exercise::Type Exercise::initVal() { return 0 ; } Exercise::Type Exercise::setVal(Type a) { val += a + initVal(); return val; }
7.36 1 2 3 4 struct X { X(int i, int j): base(i), rem(i % j){} int rem, base; }
7.37 1 2 3 4 5 6 Sales_data first_item (cin ) ; int main () Sales_data next; Sales_data last ("9-999-99999-9" ) ; }
7.38 1 Sale_data(istream& is = std ::cin ){read(is,*this );}
7.39 illegal. cause the call of overloaded ‘Sales_data()’ is ambiguous .
7.40 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Book { public : Book(unsigned isbn, std ::string const & name, std ::string const & author, std ::string const & pubdate) :isbn_(isbn), name_(name), author_(author), pubdate_(pubdate) { } explicit Book (std ::istream &in) { in >> isbn_ >> name_ >> author_ >> pubdate_; } private : unsigned isbn_; std ::string name_; std ::string author_; std ::string pubdate_; };
7.41 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 #ifndef CP5_ex7_41_h #define CP5_ex7_41_h #include <string> #include <iostream> class Sales_data { friend std ::istream &read (std ::istream &is, Sales_data &item) ; friend std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &os, const Sales_data &item) ; friend Sales_data add (const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs) public : Sales_data(const std ::string &s, unsigned n, double p):bookNo(s), units_sold(n), revenue(n*p) { std ::cout << "Sales_data(const std::string&, unsigned, double)" << std ::endl ; } Sales_data() : Sales_data("" , 0 , 0.0f ) { std ::cout << "Sales_data()" << std ::endl ; } Sales_data(const std ::string &s) : Sales_data(s, 0 , 0.0f ) { std ::cout << "Sales_data(const std::string&)" << std ::endl ; } Sales_data(std ::istream &is); std ::string isbn () const return bookNo; } Sales_data& combine (const Sales_data&) ; private : inline double avg_price () const private : std ::string bookNo; unsigned units_sold = 0 ; double revenue = 0.0 ; }; inline double Sales_data::avg_price() const { return units_sold ? revenue/units_sold : 0 ; } std ::istream &read (std ::istream &is, Sales_data &item) ;std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &os, const Sales_data &item) ;Sales_data add (const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs) ;#endif #include "ex7_41.h" Sales_data::Sales_data(std ::istream &is) : Sales_data() { std ::cout << "Sales_data(istream &is)" << std ::endl ; read(is, *this ); } Sales_data& Sales_data::combine(const Sales_data& rhs) { units_sold += rhs.units_sold; revenue += rhs.revenue; return *this ; } std ::istream &read (std ::istream &is, Sales_data &item) double price = 0 ; is >> item.bookNo >> item.units_sold >> price; item.revenue = price * item.units_sold; return is; } std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &os, const Sales_data &item) os << item.isbn() << " " << item.units_sold << " " << item.revenue; return os; } Sales_data add (const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs) Sales_data sum = lhs; sum.combine(rhs); return sum; }
7.42 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Book { public : Book(unsigned isbn, std ::string const & name, std ::string const & author, std ::string const & pubdate) :isbn_(isbn), name_(name), author_(author), pubdate_(pubdate) { } explicit Book (std ::istream &in) { in >> isbn_ >> name_ >> author_ >> pubdate_; } private : unsigned isbn_; std ::string name_; std ::string author_; std ::string pubdate_; };
7.43 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class NoDefault {public : NoDefault(int i) { } }; class C {public : C() : def(0 ) { } private : NoDefault def; }; int main () C c; std ::vector <C> vec(10 ); return 0 ; }
7.44 1 2 vector <NoDefault> vec(10 );
7.45 No problem. cause C have the default constructor.
7.46
a) A class must provide at least one constructor. (untrue , “The compiler-generated constructor is known as the synthesized default constructor.”)
b) A default constructor is a constructor with an empty parameter list. (untrue , A default constructor is a constructor that is used if no initializer is supplied.What’s more, A constructor that supplies default arguments for all its parameters also defines the default constructor)
c) If there are no meaningful default values for a class, the class should not provide a default constructor. (untrue , the class should provide.)
d) If a class does not define a default constructor, the compiler generates one that initializes each data member to the default value of its associated type. (untrue , only if our class does not explicitly define any constructors , the compiler will implicitly define the default constructor for us.)
7.47 Whether the conversion of a string to Sales_data is desired depends on how we think our users will use the conversion . In this case, it might be okay. The string in null_book probably represents a nonexistent ISBN.
Benefits:
prevent the use of a constructor in a context that requires an implicit conversion
we can define a constructor which is used only with the direct form of initialization
Drawbacks:
meaningful only on constructors that can be called with a single argument
7.48 Both are nothing happened.
7.49 1 2 3 4 5 6 (a) Sales_data &combine (Sales_data) ; (b) Sales_data &combine (Sales_data&) ; (c) Sales_data &combine (const Sales_data&) const ;
7.50 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 struct Person { friend std ::istream &read (std ::istream &is, Person &person) ; friend std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &os, const Person &person) ; public : Person() = default ; Person(const std ::string sname, const std ::string saddr):name(sname), address(saddr){ } explicit Person (std ::istream &is) this ); } std ::string getName () const return name; } std ::string getAddress () const return address; } private : std ::string name; std ::string address; }; std ::istream &read (std ::istream &is, Person &person) is >> person.name >> person.address; return is; } std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &os, const Person &person) os << person.name << " " << person.address; return os; }
7.51 Such as a function like that:
1 int getSize (const std ::vector <int >&)
if vector has not defined its single-argument constructor as explicit. we can use the function like:
What is this mean? It’s very confused.
But the std::string is different. In ordinary, we use std::string to replace const char *(the C language). so when we call a function like that:
1 2 void setYourName (std ::string ) setYourName("pezy" );
it is very natural.
7.52 1 2 3 4 5 struct Sales_data { std ::string bookNo; unsigned units_sold; double revenue; };
7.53 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Debug {public : constexpr Debug(bool b = true) : rt(b), io(b), other(b) { } constexpr Debug(bool r, bool i, bool o) : rt(r), io(i), other(o) { } constexpr bool any () return rt || io || other; } void set_rt (bool b) void set_io (bool b) void set_other (bool b) private : bool rt; bool io; bool other; };
7.54 In C++11, constexpr member functions are implicitly const, so the “set_xx” functions, which will modify data members, cannot be declared as constexpr.
In C++14, this property no longer holds, so constexpr is suitable.
7.55 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <string> #include <iostream> #include <type_traits> struct Data { int ival; std ::string s; }; int main () std ::cout << std ::boolalpha; std ::cout << std ::is_literal_type<Data>::value << std ::endl ; }
7.56
What is a static class member?
A class member that is associated with the class , rather than with individual objects of the class type.
What are the advantages of static members?
each object can no need to store a common data. And if the data is changed, each object can use the new value.
How do they differ from ordinary members?
a static data member can have incomplete type .
we can use a static member as a default argument .
7.57 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Account {public : void calculate () static double rate () return interestRate; } static void rate (double newRate) private : std ::string owner; double amount; static double interestRate; static constexpr double todayRate = 42.42 ; static double initRate () return todayRate; } }; double Account::interestRate = initRate();
7.58 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Example {public : static double rate = 6.5 ; static const int vecSize = 20 ; static vector <double > vec(vecSize); }; #include "example.h" double Example::rate;vector <double > Example::vec;class Example {public : static constexpr double rate = 6.5 ; static const int vecSize = 20 ; static vector <double > vec; }; #include "example.h" constexpr double Example::rate;vector <double > Example::vec(Example::vecSize);
第八章 8.1 1 2 3 4 5 6 istream& fun (istream& is) { string buf; while (is >> buf) cout << buf << endl ; is.clear(); }
8.2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 istream& fun (istream& is) { string buf; while (is >> buf) cout << buf << endl ; is.clear(); } int main () istream& is = fun(cin ); cout << is.rdstate() << endl ; return 0 ; }
8.3 putting cin in an error state cause to terminate. such as eofbit, failbit and badbit.
8.4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 vector <string > vec;void fun (string fileName) ifstream f1 (fileName) ; if (f1){ string a; while (getline(f1, a)){ vec.push_back(a); } }else cerr << "can not open the file : " << fileName << endl ; }
8.5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 vector <string > vec;void fun (string fileName) ifstream f1 (fileName) ; if (f1){ string a; while (f1 >> a){ vec.push_back(a); } }else cerr << "can not open the file : " << fileName << endl ; }
8.6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 #include "../ch07/ex7_26.h" using std ::ifstream; using std ::cout ; using std ::endl ; using std ::cerr ;int main (int argc, char **argv) ifstream input (argv[1 ]) ; Sales_data total; if (read(input, total)) { Sales_data trans; while (read(input, trans)) { if (total.isbn() == trans.isbn()) total.combine(trans); else { print(cout , total) << endl ; total = trans; } } print(cout , total) << endl ; } else cerr << "No data?!" << endl ; return 0 ; }
8.7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include "../ch07/ex7_26.h" using std ::ifstream; using std ::ofstream; using std ::endl ; using std ::cerr ;int main (int argc, char **argv) ifstream input (argv[1 ]) ; ofstream output (argv[2 ]) ; Sales_data total; if (read(input, total)) { Sales_data trans; while (read(input, trans)) { if (total.isbn() == trans.isbn()) total.combine(trans); else { print(output, total) << endl ; total = trans; } } print(output, total) << endl ; } else cerr << "No data?!" << endl ; return 0 ; }
8.8 1 ofstream output (argv[2 ], ofstream::app) ;
8.9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 istream& fun (istream& is) { string buf; while (is >> buf) cout << buf << endl ; is.clear(); } int main () istringstream iss ("ATest" ) fun(iss); return 0 ; }
8.10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 string fname,line;vector <string > vec;ifstream ifs (fname) ;if (!ifs){ cerr << "No data" << endl ; exit (0 ); } while (getline(ifs,line)) vec.push_back(line); for (auto &s : vec){ istringstream iss (s) string s; while (iss >> s) cout << s << endl ; }
8.11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ;struct PersonInfo { string name; vector <string > phones; }; int main () string line, word; vector <PersonInfo> people; istringstream record; while (getline(cin , line)) { PersonInfo info; record.clear(); record.str(line); record >> info.name; while (record >> word) info.phones.push_back(word); people.push_back(info); } for (auto &p : people) { std ::cout << p.name << " " ; for (auto &s : p.phones) std ::cout << s << " " ; std ::cout << std ::endl ; } return 0 ; }
8.12 Cause we need a aggregate class here. so it should have no in-class initializers.
8.13 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ;struct PersonInfo { string name; vector <string > phones; }; bool valid (const string & str) return isdigit (str[0 ]); } string format (const string & str) return str.substr(0 ,3 ) + "-" + str.substr(3 ,3 ) + "-" + str.substr(6 ); } int main () ifstream ifs ("../data/phonenumbers.txt" ) ; if (!ifs) { cerr << "no phone numbers?" << endl ; return -1 ; } string line, word; vector <PersonInfo> people; istringstream record; while (getline(ifs, line)) { PersonInfo info; record.clear(); record.str(line); record >> info.name; while (record >> word) info.phones.push_back(word); people.push_back(info); } for (const auto &entry : people) { ostringstream formatted, badNums; for (const auto &nums : entry.phones) if (!valid(nums)) badNums << " " << nums; else formatted << " " << format(nums); if (badNums.str().empty()) cout << entry.name << " " << formatted.str() << endl ; else cerr << "input error: " << entry.name << " invalid number(s) " << badNums.str() << endl ; } return 0 ; }
8.14
cause they are all class type, not the built-in type. so reference more effective.
output shouldn’t change their values. so we added the const.
第九章 9.1 list & deque & vector
9.2 9.3 two iterators, begin and end:
they refer to elements of the same container.
It is possible to reach end by repeatedly incrementing begin.
9.4 1 2 3 4 5 6 bool fun (vector <int >::iterator begin, vector <int >::iterator end, int val) for (; begin!=end; begin++) if (*begin == val) return true ; return false ; }
9.5 1 2 3 4 5 6 vector <int >::iterator fun (vector <int >::iterator begin, vector <int >::iterator end, int val) { for (; begin!=end; begin++) if (*begin == val) return begin; return end; }
9.6 1 2 3 4 list <int > lst1;list <int >::iterator iter1 = lst1.begin(), iter2 = lst1.end();while (iter1 != iter2);
9.7 9.8 1 2 list <string >::const_iterator cit;list <string >::iterator it;
9.9 cbegin is a const member that returns the container’s const_iterator type.
begin is nonconst and returns the container’s iterator type.
9.10 1 2 3 4 vector <int > v1;const vector <int > v2;auto it1 = v1.begin();auto it2 = v2.begin(), it3 = v1.cbegin(), it4 = v2.cbegin();
9.11 1 2 3 4 5 6 vector <int > vec; vector <int > vec(10 ); vector <int > vec(10 , 1 ); vector <int > vec{1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 }; vector <int > vec(other_vec); vector <int > vec(other_vec.begin(), other_vec.end());
9.12 The constructor that takes another container as an argument (excepting array) assumes the container type and element type of both containers are identical. It will also copy all the elements of the received container into the new one:
1 2 3 4 list <int > numbers = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 };list <int > numbers2(numbers); vector <int > numbers3(numbers); list <double > numbers4(numbers);
The constructor that takes two iterators as arguments does not require the container types to be identical. Moreover, the element types in the new and original containers can differ as long as it is possible to convert the elements we’re copying to the element type of the container we are initializing. It will also copy only the object delimited by the received iterators.
1 2 3 4 5 list <int > numbers = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 };list <int > numbers2(numbers.begin(), numbers.end); vector <int > numbers3(numbers.begin(), --numbers.end()); list <double > numbers4(++numbers.beg(), --numbers.end()); forward_list<float > numbers5(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
9.13 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ;int main () list <int > a(10 , 1 ); vector <double > a1(a.begin(), a.end()); vector <int > b(10 , 2 ); vector <double > b1(b.begin(), b.end()); return 0 ; }
9.14 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ;typedef long long ll;const int N = 2e6 + 5 ;ll num[N]; int main () list <char *> a{"Mooophy" , "pezy" , "Queeuqueg" }; vector <string > b; b.assign(a.cbegin(), a.cend()); for (auto &it : b) cout << it << endl ; return 0 ; }
9.15 1 2 3 4 5 6 vector <int > a;vector <int > b;if (a == b) puts ("Yes" ); else puts ("No" );
9.16 1 2 3 list <int > li{ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 };vector <int > vec{ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 };cout << (vector <int >(li.begin(), li.end()) == vec ? "true" : "false" ) << endl ;
9.17 必须有相同的容器和相同的类型,所持有的类型必须支持关系操作。
9.18 1 2 3 4 5 6 string s;deque <string > de;while (cin >> s) de.push_back(s); for (auto it = de.cbegin(); it != de.cend(); it++) cout << *it << endl ;
9.19 1 2 3 4 5 6 string s;list <string > li;while (cin >> s) li.push_back(s); for (auto it = li.cbegin(); it != li.cend(); it++) cout << *it << endl ;
9.20 1 2 3 4 list <int > li{ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 };deque <int > odd, even;for (auto i : li) (i & 0x1 ? odd : even).push_back(i);
9.21 第一个 insert 调用接受刚读取的字符串,并将其放在 iter 所表示的元素的前面,insert 返回的值是指向这个新元素的迭代器。将该迭代器赋值给 iter,然后重复 while ,读取另一个单词。
只要有单词要插入,每次遍历 while 都会在 iter 前面插入一个新元素,并将新插入元素的位置重新赋值给 iter 即可。
9.22 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 vector <int >::iterator iter = iv.begin(), mid = iv.begin + iv.size()/2 ;while (iter != mid) if (*iter == some_val) mid = iv.insert(iter, 2 * some_val); void double_and_insert (std ::vector <int >& v, int some_val) auto mid = [&]{ return v.begin() + v.size() / 2 ; }; for (auto curr = v.begin(); curr != mid(); ++curr) if (*curr == some_val) ++(curr = v.insert(curr, 2 * some_val)); } int main () std ::vector <int > v{ 1 , 9 , 1 , 9 , 9 , 9 , 1 , 1 }; double_and_insert(v, 1 ); for (auto i : v) std ::cout << i << std ::endl ; }
9.23 同一个元素
9.24 1 2 3 4 5 6 vector <int > a;a.at(0 ), a[0 ], a.front(), a.end();
9.25 不会发生什么事情 & 从 elem1 删到最后 & 同首
9.26 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 int ia[] = { 0 , 1 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 , 8 , 13 , 21 , 55 , 89 };vector <int > a(ia, end(ia));list <int > b(a.begin(), a.end());auto it = b.begin();while (it != b.end()) if (*it & 0x1 ) it = b.erase(it); else it++; auto i = a.begin();while (i != a.end()) if (!(*it & 0x1 )) i = a.erase(it); else i++;
9.27 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 auto remove_odds (forward_list<int >& flist) auto is_odd = [] (int i) { return i & 0x1 ; }; flist.remove_if(is_odd); } int main () forward_list<int > data { 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 }; remove_odds(data); for (auto i : data) cout << i << " " ; return 0 ; }
9.28 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 auto fun (forward_list<string > &lst, string &a, string &b) auto prev = lst.before_begin(); for (auto curr = lst.begin(); curr != lst.end(); prev = curr++) { if (*curr == to_find) { lst.insert_after(curr, to_add); return ; } } lst.insert_after(prev, to_add); }
9.29 1 2 vec.resize(100 ); vec.resize(10 );
9.30 有默认的初始化或者相应的构造函数
9.31 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 auto remove_evens_and_double_odds (list <int >& data) for (auto cur = data.begin(); cur != data.end();) if (*cur & 0x1 ) cur = data.insert(cur, *cur), advance(cur, 2 ); else cur = data.erase(cur); } int main () list <int > data { 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 }; remove_evens_and_double_odds(data); for (auto i : data) cout << i << " " ; return 0 ; } auto remove_evens_and_double_odds (forward_list<int >& data) for (auto cur = data.begin(), prv = data.before_begin(); cur != data.end();) if (*cur & 0x1 ) cur = data.insert_after(prv, *cur), advance(cur, 2 ), advance(prv, 2 ); else cur = data.erase_after(prv); } int main () forward_list<int > data { 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 }; remove_evens_and_double_odds(data); for (auto i : data) cout << i << " " ; return 0 ; }
9.32 the statement is illegal, because as said in Standard [5.2.2] : “The order of evaluation of arguments is unspecified.” As a result, after entering function insert, iter could be its original value or original value + 1 or even anything else, depending on how compiler implemented.
9.33 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 vector <int > v{ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 };auto begin = v.begin();while (begin != v.end()) { ++begin; v.insert(begin, 42 ); ++begin; } for (auto i : v) cout << i << " " ;
9.34 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 iter = vi.begin(); while (iter != vi.end()) if (*iter % 2 ) iter = vi.insert(iter, *iter); ++iter; vector <int > data { 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 };for (auto cur = data.begin(); cur != data.end(); ++cur) if (*cur & 0x1 ) cur = data.insert(cur, *cur), ++cur; for (auto i : data) cout << i << " " ;
9.35 size 是目前保存的元素数量
capacity 是在必须重新申请内存之前能存储的最大元素数量
9.36 not
9.37 list 不连续存储数据
array 是固定的大小
9.38 1 2 3 vector <string > v;for (string buffer; cin >> buffer; v.push_back(buffer)) cout << v.capacity() << endl ;
9.39 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 vector <string > svec;svec.reserve(1024 ); string word;while (cin >> word) svec.push_back(word); svec.resize(svec.size() + svec.size()/2 );
9.40
read
size
capacity
256
384
1024
512
768
1024
1000
1500
2000(clang is 2048)
1048
1572
2048
9.41 1 2 3 vector <char > v{ 'h' , 'e' , 'l' , 'l' , 'o' };string str (v.cbegin(), v.cend()) cout << str << endl ;
9.42 str.reserve(120)
9.43 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 void replace_with (string &s, string const & oldVal, string const & newVal) for (auto cur = s.begin(); cur <= s.end() - oldVal.size(); ) if (oldVal == string { cur, cur + oldVal.size() }) cur = s.erase(cur, cur + oldVal.size()), cur = s.insert(cur, newVal.begin(), newVal.end()), cur += newVal.size(); else ++cur; } int main () string s{ "To drive straight thru is a foolish, tho courageous act." }; replace_with(s, "tho" , "though" ); replace_with(s, "thru" , "through" ); cout << s << endl ; return 0 ; }
9.44 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 void replace_with (string &s, string const & oldVal, string const & newVal) for (size_t pos = 0 ; pos <= s.size() - oldVal.size();) if (s[pos] == oldVal[0 ] && s.substr(pos, oldVal.size()) == oldVal) s.replace(pos, oldVal.size(), newVal), pos += newVal.size(); else ++pos; } int main () string s{ "To drive straight thru is a foolish, tho courageous act." }; replace_with(s, "tho" , "though" ); replace_with(s, "thru" , "through" ); cout << s << endl ; return 0 ; }
9.45 1 2 3 4 string fun (string s, string const & a, string const & b) s.insert(s.begin, a.begin(), a.end()); return s.append(b); }
9.46 1 2 3 4 5 6 string fun (string s, string const & pre, string const & su) s.insert(0 , pre); s.insert(s.size(), su); return s; }
9.47 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 string numbers{ "123456789" };string alphabet{ "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ" };string str{ "ab2c3d7R4E6" };cout << "numeric characters: " ;for (int pos = 0 ; (pos = str.find_first_of(numbers, pos)) != string ::npos; ++pos) cout << str[pos] << " " ; cout << "\nalphabetic characters: " ;for (int pos = 0 ; (pos = str.find_first_of(alphabet, pos)) != string ::npos; ++pos) cout << str[pos] << " " ; cout << endl ;string numbers{ "0123456789" };string alphabet{ "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ" };string str{ "ab2c3d7R4E6" };cout << "numeric characters: " ;for (int pos = 0 ; (pos = str.find_first_not_of(alphabet, pos)) != string ::npos; ++pos) cout << str[pos] << " " ; cout << "\nalphabetic characters: " ;for (int pos = 0 ; (pos = str.find_first_not_of(numbers, pos)) != string ::npos; ++pos) cout << str[pos] << " " ; cout << endl ;
9.48 string::npos
9.49 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ifstream ifs ("../data/letter.txt" ) ;if (!ifs) return -1 ;string longest;auto update_with = [&longest](string const & curr){ if (string ::npos == curr.find_first_not_of("aceimnorsuvwxz" )) longest = longest.size() < curr.size() ? curr : longest; }; for (string curr; ifs >> curr; update_with(curr));cout << longest << endl ;
9.50 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 auto sum_for_int (vector <string > const & v) int sum = 0 ; for (auto const & s : v) sum += stoi(s); return sum; } auto sum_for_float (vector <string > const & v) float sum = 0.0 ; for (auto const & s : v) sum += stof(s); return sum; } int main () vector <string > v = { "1" , "2" , "3" , "4.5" }; cout << sum_for_int(v) << endl ; cout << sum_for_float(v) << endl ; return 0 ; }
9.51 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 using namespace std ;class My_date {private : unsigned year, month, day; public : My_date(const string &s){ unsigned tag; unsigned format; format = tag = 0 ; if (s.find_first_of("/" )!= string :: npos) { format = 0x01 ; } if ((s.find_first_of(',' ) >= 4 ) && s.find_first_of(',' )!= string :: npos){ format = 0x10 ; } else { if (s.find_first_of(' ' ) >= 3 && s.find_first_of(' ' )!= string :: npos){ format = 0x10 ; tag = 1 ; } } switch (format){ case 0x01 : day = stoi(s.substr(0 , s.find_first_of("/" ))); month = stoi(s.substr(s.find_first_of("/" ) + 1 , s.find_last_of("/" )- s.find_first_of("/" ))); year = stoi(s.substr(s.find_last_of("/" ) + 1 , 4 )); break ; case 0x10 : if ( s.find("Jan" ) < s.size() ) month = 1 ; if ( s.find("Feb" ) < s.size() ) month = 2 ; if ( s.find("Mar" ) < s.size() ) month = 3 ; if ( s.find("Apr" ) < s.size() ) month = 4 ; if ( s.find("May" ) < s.size() ) month = 5 ; if ( s.find("Jun" ) < s.size() ) month = 6 ; if ( s.find("Jul" ) < s.size() ) month = 7 ; if ( s.find("Aug" ) < s.size() ) month = 8 ; if ( s.find("Sep" ) < s.size() ) month = 9 ; if ( s.find("Oct" ) < s.size() ) month =10 ; if ( s.find("Nov" ) < s.size() ) month =11 ; if ( s.find("Dec" ) < s.size() ) month =12 ; char chr = ',' ; if (tag == 1 ){ chr = ' ' ; } day = stoi(s.substr(s.find_first_of("123456789" ), s.find_first_of(chr) - s.find_first_of("123456789" ))); year = stoi(s.substr(s.find_last_of(' ' ) + 1 , 4 )); break ; } } void print () cout << "day:" << day << " " << "month: " << month << " " << "year: " << year; } }; int main () My_date d ("Jan 1 1900" ) ; d.print(); return 0 ; }
9.52 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 int main () string expression{ "This is (pezy)." }; bool bSeen = false ; stack <char > stk; for (const auto &s : expression) { if (s == '(' ) { bSeen = true ; continue ; } else if (s == ')' ) bSeen = false ; if (bSeen) stk.push(s); } string repstr; while (!stk.empty()) { repstr += stk.top(); stk.pop(); } expression.replace(expression.find("(" )+1 , repstr.size(), repstr); cout << expression << endl ; return 0 ; }
第十章 10.1 & 10.2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 vector <int > vec{ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 6 , 6 , 2 };cout << count(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 6 );list <string > v = { "aa" , "aaa" , "aa" , "cc" };cout << count(v.begin(), v.end(), "aa" );
10.3 &10.4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 vector <int > vec{ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 6 , 6 , 2 };int sum = accumulate(vec.cbegin(), vec.end(), 0 );vector <double > vd = { 1.1 , 0.5 , 3.3 };cout << accumulate(vd.cbegin(), vd.cend(), 0 )<<endl ;
10.5 For such case, std::equal is going to compare the address value rather than the string value. So the result is not the same as std::string. Try to avoid coding this way. Check #227 for more detail.
10.6 1 2 vector <int > vec{ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 6 , 6 , 2 };fill_n(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 0 );
10.7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 vector <int > vec; list <int > lst; int i;while (cin >> i) lst.push_back(i); copy(lst.cbegin(), lst.cend(), back_inserter(vec)); vector <int > vec;vec.reserve(10 ); fill_n(vec.begin(), 10 , 0 );
10.8 Inserters like back_inserter is part of <iterator> rather than <algorithm>.
10.9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 template <typename Sequence>auto println(Sequence const& seq) -> std::ostream& { for (auto const & elem : seq) std ::cout << elem << " " ; return std ::cout << std ::endl ; } void elimDups (vector <int > &a) sort(a.begin(), a.end()); println(vs); auto end = unique(a.begin(), a.end()); println(vs); a.erase(end, a.end()); println(vs); }
10.10 将算法与容器分离开
10.11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 template <typename Sequence>inline ostream& println (Sequence const & seq) for (auto const & elem : seq) cout << elem << " " ; cout << endl ; return cout ; } inline bool is_shorter (string const & lhs, string const & rhs) return lhs.size() < rhs.size(); } void elimdups (vector <string > &vs) sort(vs.begin(), vs.end()); auto new_end = unique(vs.begin(), vs.end()); vs.erase(new_end, vs.end()); } int main () vector <string > v{ "1234" , "1234" , "1234" , "Hi" , "alan" , "wang" }; elimdups(v); stable_sort(v.begin(), v.end(), is_shorter); println(v); return 0 ; }
10.12 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 #include "../ch07/ex7_26.h" inline bool compareIsbn (const Sales_data &sd1, const Sales_data &sd2) return sd1.isbn().size() < sd2.isbn().size(); } int main () Sales_data d1("aa"), d2("aaaa"), d3("aaa"), d4("z"), d5("aaaaz"); vector <Sales_data> v{ d1, d2, d3, d4, d5 }; sort(v.begin(), v.end(), compareIsbn); for (const auto &element : v) cout << element.isbn() << " " ; cout << endl ; return 0 ; }
10.13 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 bool predicate (const string &s) return s.size() >= 5 ; } int main () auto v = vector <string >{ "a" , "as" , "aasss" , "aaaaassaa" , "aaaaaabba" , "aaa" }; auto pivot = partition(v.begin(), v.end(), predicate); for (auto it = v.cbegin(); it != pivot; ++it) cout << *it << " " ; cout << endl ; return 0 ; }
10.14 1 auto add = [](int a, int b){return a + b;}
10.15 1 2 int a = 1 ;auto add = [a](int b){return a + b;}
10.16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 void biggies (vector <string > &s, vector <string >::size_type sz) sort(s.begin(), s.end(),[](const string &s1, const string &s2){ return s1 < s2; }); auto end = unique(s.begin(), s.end()); s.erase(end, s.end()); auto wc = find_if(s.begin(), s.end(), [sz](const string &s1){ return s1.size() >= sz; }); auto cc = s.end() - wc; cout << count << " " << make_plural(cc, "word" , "s" ) << " of length " << sz << " or longer " << endl ; for_each(wc, s.end(), [](const string &s1){ cout << s1 << endl ; }); }
10.17 1 2 3 sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [](const Sales_data &a, const Sales_data &b){ return a.isbn().size() < b.isbn().size(); });
10.18 & 10.19 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 void elimdups (vector <string > &vs) sort(vs.begin(), vs.end()); auto new_end = unique(vs.begin(), vs.end()); vs.erase(new_end, vs.end()); } void biggies_partition (vector <string > &vs, size_t sz) elimdups(vs); auto pivot = partition(vs.begin(), vs.end(), [sz](const string &s){ return s.size() >= sz;} ); for (auto it = vs.cbegin(); it != pivot; ++it) std ::cout << *it << " " ; } void biggies_stable_partition (vector <string > &vs, size_t sz) elimdups(vs); auto pivot = stable_partition(vs.begin(), vs.end(), [sz](const string & s){ return s.size() >= sz; }); for (auto it = vs.cbegin(); it != pivot; ++it) std ::cout << *it << " " ; } int main () vector <string > v{ "the" , "quick" , "red" , "fox" , "jumps" , "over" , "the" , "slow" , "red" , "turtle" }; cout << "ex10.18: " ; vector <string > v1(v); biggies_partition(v1, 4 ); cout << endl ; cout << "ex10.19: " ; vector <string > v2(v); biggies_stable_partition(v2, 4 ); cout << endl ; return 0 ; }
10.20 & 10.21 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 auto count = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), [](const string &s){ return s.size() > 6 ; }); int i = 9 ;auto what = [i](){return i > 0 ? --i : !i};
10.22 1 2 3 4 5 bool isLesserThanOrEqualTo6 (const string &s, string ::size_type sz) return s.size() <= sz; } sort(v.begin(), v.end(), bind(isLesserThanOrEqualTo6(_1, 6 )));
10.23 Assuming the function to be bound have n parameters, bind take n + 1 parameters. The additional one is for the function to be bound itself.
10.24 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 auto check_size (string const & str, size_t sz) return str.size() < sz; } int main () vector <int > vec{ 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 }; string str ("123456" ) auto result = find_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), bind(check_size, str, _1)); if (result != vec.end()) cout << *result << endl ; else cout << "Not found" << endl ; return 0 ; }
10.25 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 void elimdups (vector <string > &vs) sort(vs.begin(), vs.end()); vs.erase(unique(vs.begin(), vs.end()), vs.end()); } bool check_size (const string &s, string ::size_type sz) return s.size() >= sz; } void biggies (vector <string > &words, vector <string >::size_type sz) elimdups(words); auto iter = stable_partition(words.begin(), words.end(), bind(check_size, _1, sz)); for_each(words.begin(), iter, [](const string &s){ cout << s << " " ; }); } int main () vector <string > v{ "the" , "quick" , "red" , "fox" , "jumps" , "over" , "the" , "slow" , "red" , "turtle" }; biggies(v, 4 ); }
10.26
back_inserter uses push_back.front_inserter uses push_front.insert uses insert
10.27 1 2 3 vector <int > vec{ 1 , 1 , 3 , 3 , 5 , 5 , 7 , 7 , 9 };list <int > lst;unique_copy(vec.begin(), vec.end(), back_inserter(lst));
10.28 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 template <typename Sequence>void print (Sequence const & seq) for (const auto & i : seq) cout << i << " " ; cout << endl ; } int main () vector <int > vec{ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 }; list <int > lst1; copy(vec.cbegin(), vec.cend(), inserter(lst1, lst1.begin())); print(lst1); list <int > lit2; copy(vec.cbegin(), vec.cend(), back_inserter(lit2)); print(lit2); list <int > lst3; copy(vec.cbegin(), vec.cend(), front_inserter(lst3)); print(lst3); }
10.29 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ifstream fin ("D:\\WorkSpace\\C++\\data\\book.txt" ) ;if (!fin) cout << "yes" << endl ; istream_iterator<string > in(fin), eof; vector <string > vec;copy(in, eof, back_inserter(vec)); copy(vec.cbegin(), vec.cend(), ostream_iterator<string >(cout , "\n" ));
10.30 1 2 3 vector <int > vec(istream_iterator<int >(std ::cin ), istream_iterator<int >());sort(vec.begin(), vec.end()); copy(vec.cbegin(), vec.cend(), ostream_iterator<int >(cout , " " ));
10.31 1 2 3 4 5 6 istream_iterator<int > in_iter(cin ), eof; vector <int > vec;while (in_iter != eof) vec.push_back(*in_iter++); sort(vec.begin(), vec.end()); unique_copy(vec.cbegin(), vec.cend(), ostream_iterator<int >(cout , " " ));
10.32 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 istream_iterator<Sales_item> in_iter(cin ), in_eof; vector <Sales_item> vec;while (in_iter != in_eof) vec.push_back(*in_iter++); sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), compareIsbn); for (auto beg = vec.cbegin(), end = beg; beg != vec.cend(); beg = end){ end = find_if(beg, vec.cend(), [beg](const Sales_item &item) { return item.isbn() != beg->isbn(); }); cout << accumulate(beg, end, Sales_item(beg->isbn())) << endl ; }
10.33 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 int main (int argc, char **argv) if (argc != 4 ) return -1 ; ifstream ifs (argv[1 ]) ; ofstream ofs_odd(argv[2]), ofs_even(argv[3]); istream_iterator<int > in(ifs), in_eof; ostream_iterator<int > out_odd(ofs_odd, " " ), out_even(ofs_even, "\n" ); for_each(in, in_eof, [&out_odd, &out_even](const int i){ (i & 0x1 ? out_odd : out_even) = i; }); return 0 ; }
10.34 ~ 10.37 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 vector <int > vec = { 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 };for (auto it = vec.crbegin(); it != vec.crend(); it++) cout << *it << endl ; for (auto it = vec.cend();;){ cout << *(--it) << endl ; if (it == vec.cbegin()) break ; } list <int > lst = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 0 , 5 , 6 };auto last = find(lst.crbegin(), lst.crend(), 0 );cout << distance(last, lst.crend());copy(vec.cbegin() + 3 , vec.cbegin() + 7 , lst.rbegin());
10.38
Input iterators : ==, !=, ++, *, ->
Output iterators : ++, *
Forward iterators : ==, !=, ++, *, ->
Bidirectional iterators : ==, !=, ++, --, *, ->
Random-access iterators : ==, !=, <, <=, >, >=, ++, --, +, +=, -, -=, -(two iterators), *, ->, iter[n] == * (iter + n)
10.39 list have the Bidirectional iterators .
vector have the Random-access iterators .
10.40
copy : first and second are Input iterators, last is Output iterators.reverse : Bidirectional iterators.unique : Forward iterators.
10.41 1 2 3 4 replace(beg, end, old_val, new_val); replace_if(beg, end, pred, new_val); replace_copy(beg, end, dest, old_val, new_val); replace_copy_if(beg, end, dest, pred, new_val);
10.42 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 void elimDups (list <string > &words) words.sort(); words.unique(); } int main () list <string > l = { "aa" , "aa" , "aa" , "aa" , "aasss" , "aa" }; elimDups(l); for (const auto & e : l) cout << e << " " ; cout << endl ; }
第十一章 11.1 map : 关联容器,元素根据键值对存储和检索,二叉搜索树实现
vector : 顺序容器,元素按其在容器中的位置顺序存储和访问,动态数组实现
11.2 list : 不需要随机访问数据,但希望在容器的任何位置(例如内存管理分配器中)快速插入或删除数据。
vector : 连续存储和处理一组数据时,支持随机访问和末尾的快速插入和删除。
deque : FIFO。
map : 将相关信息配对时使用映射,需要在大量数据中查找pair时。
set : 创建一个有序对象的列表(树),以便快速遍历/搜索时。
11.3 1 2 3 4 5 void fun (map <string , size_t > &mp, vector <string > words) for (auto s:words) ++mp[s]; }
11.4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 auto strip(string& str) -> string const& { for (auto & ch : str) ch = tolower (ch); str.erase(remove_if(str.begin(), str.end(), ispunct ), str.end()); return str; } void fun (map <string , size_t > &mp, vector <string > words) for (auto s:words) ++mp[strip(s)]; }
11.5 map vs set
形成字符串有序集就直接用 set ,如果还想知道每个字符的含义,比如出现次数,就用 map
11.6 list vs set
set 单一有序,list 可重复无序
11.7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 using Families = map <string , vector <string >>;auto make_families () Families families; for (string ln; cout << "Last name:\n" , cin >> ln && ln != "@q" ;) for (string cn; cout << "|-Children's names:\n" , cin >> cn && cn != "@q" ;) families[ln].push_back(cn); return families; } auto print (Families const & families) for (auto const & family : families) { cout << family.first << ":\n" ; for (auto const & child : family.second) cout << child << " " ; cout << "\n" ; } } int main () print(make_families()); return 0 ; }
11.8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 int main () vector <string > exclude = { "aa" , "bb" , "cc" , "dd" , "ee" , "ff" }; for (string word; cout << "Enter plz:\n" , cin >> word; ) { auto is_excluded = binary_search(exclude.cbegin(), exclude.cend(), word); auto reply = is_excluded ? "excluded" : "not excluded" ; cout << reply << endl ; } return 0 ; }
11.9 & 11.10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 map <string , list <size_t >> mp;map <vector <int >::iterator, int > mvt;map <list <int >::iterator, int > mlt;vector <int > vi;mv.insert(pair<vector <int >::iterator, int >(vi.begin(), 0 )); list <int > li;ml.insert(pair<list <int >::iterator, int >(li.begin(), 0 ));
11.11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 #include "../ch07/ex7_26.h" #include <set> auto less (Sales_data const & lhs, Sales_data const & rhs) return lhs.isbn() < rhs.isbn(); } int main () using Less = bool (*)(Sales_data const &, Sales_data const &); multiset <Sales_data, Less> bookstore(less); return 0 ; }
11.12 & 11.13 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 vector <pair<string , int >> vec;void fun (vector <string > &s, vector <int > &a) for (int i = 0 ; i<s.size() && i < a.size();i++) vec.push_back({s[i],a[i]}); }
11.14 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Families { public : using Child = pair<string , string >; using Children = vector <Child>; using Data = map <string , Children>; auto add (string const & last_name, string const & first_name, string birthday) { auto child = make_pair(first_name, birthday); _data[last_name].push_back(child); } auto print () const { for (auto const & pair : _data) { cout << pair.first << ":\n" ; for (auto const & child : pair.second) cout << child.first << " " << child.second << endl ; cout << endl ; } } private : Data _data; }; int main () Families families; auto msg = "Please enter last name, first name and birthday:\n" ; for (string l, f, b; cout << msg, cin >> l >> f >> b; families.add(l, f, b)); families.print(); return 0 ; }
11.15 1 2 3 4 map <int , vector <int >> mp;
11.16 1 2 3 4 map <int , string > mp;mp[1 ] = "hello" ; auto it = mp.cbegin();string s = it->second;
11.17 1 2 3 4 5 6 muliset<string > c; vector <string > v;copy(v.begin(), v.end(), inserter(c, c.end())); copy(v.begin(), v.end(), back_inserter(c)); copy(c.begin(), c.end(), inserter(v, v.end())); copy(c.begin(), c.end(), back_inserter(v));
11.18 map<string, size_t>::const_iterator
11.19 1 2 3 using compareType = bool (*)(const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs);multiset <Sales_data, compareType> bookstore(compareIsbn);multiset <Sales_data, compareType>::iterator c_it = bookstore.begin();
11.20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 map <string , size_t > counts;for (string word; cin >> word;){ auto result = counts.insert({ word, 1 }); if (!result.second) ++result.first->second; } for (auto const & count : counts) cout << count.first << " " << count.second << ((count.second > 1 ) ? " times\n" : " time\n" );
11.21 1 2 3 4 map <string , size_t > word_count;string word;while (cin >> word) ++word_count.insert({word, 0 }).first->second;
11.22 map<string, int>
pair<map<string, vector<int>>, bool>
11.23 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 int main () multimap <string , string > families; for (string lname, cname; cin >> cname >> lname; families.emplace(lname, cname)); for (auto const & family : families) cout << family.second << " " << family.first << endl ; }
11.24 ~ 11.26 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 map <int , int > m;m[0 ] = 1 ; vector <int > v;v[0 ] = 1 ; map <int , string > m = { { 1 ,"ss" },{ 2 ,"sz" } };using KeyType = map <int , string >::key_type;cout << "type to subscript: " << typeid (KeyType).name() << endl ;cout << "returned from the subscript operator: " << typeid (decltype (m[1 ])).name();
11.27 ~ 11.30 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 map <string , vector <int >> mp;auto it = mp.find(name);pos; pos.first; pos.first->second;
11.31 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 multimap <string , string > authors{ { "alan" , "DMA" }, { "pezy" , "LeetCode" }, { "alan" , "CLRS" }, { "wang" , "FTP" }, { "pezy" , "CP5" }, { "wang" , "CPP-Concurrency" } }; string author = "pezy" ;string work = "CP5" ;auto found = authors.find(author);auto count = authors.count(author);while (count) { if (found->second == work) { authors.erase(found); break ; } ++found; --count; } for (const auto &author : authors) std ::cout << author.first << " " << author.second << std ::endl ;
11.32 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 multimap <string , string > authors{ { "alan" , "DMA" }, { "pezy" , "LeetCode" }, { "alan" , "CLRS" }, { "wang" , "FTP" }, { "pezy" , "CP5" }, { "wang" , "CPP-Concurrency" } }; map <string , multiset <string >> order_authors;for (const auto &author : authors) order_authors[author.first].insert(author.second); for (const auto &author : order_authors) { cout << author.first << ": " ; for (const auto &work : author.second) cout << work << " " ; cout << endl ; }
11.33 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ;map <string , string > buildMap(ifstream &map_file){ map <string , string > trans_map; for (string key, value; map_file >> key && getline(map_file, value); ) if (value.size() > 1 ) trans_map[key] = value.substr(1 ).substr(0 , value.find_last_not_of(' ' )); return trans_map; } const string & transform (const string &s, const map <string , string > &m) auto map_it = m.find(s); return map_it == m.cend() ? s : map_it->second; } void word_transform (ifstream &map , ifstream &input) auto trans_map = buildMap(map ); for (string text; getline(input, text); ) { istringstream iss (text) for (string word; iss >> word; ) cout << transform(word, trans_map) << " " ; cout << endl ; } } int main () ifstream ifs_map ("../data/word_transformation_bad.txt" ) ; ifstream ifs_content ("../data/given_to_transform.txt" ) ; if (ifs_map && ifs_content) word_transform(ifs_map, ifs_content); else cerr << "can't find the documents." << endl ; }
11.34 可能会创建原先不存在的键值对
11.35
use subscript operator: if a word does appear multiple times, our loops will put the last corresponding phrase into trans_map
use insert: if a word does appear multiple times, our loops will put the first corresponding phrase into trans_map
11.36 不会被替换,因为替换规则首先得满足 value.size() > 1
11.37
Ordered Associative Container
Standard Traversal encounters elements in sorted order
Order predicate may be specified
Default order predicate is “less than”, defined using operator< for the element type
Popular implementations: OrderedVector, BinarySearchTree
Search operations required to have O(log n ) runtime
Insert, Remove operations should either be seldom used or have O(log n ) runtime
Unordered Associative Container
Standard Traversal encounters elements in unspecified order
Search, Insert, Remove operations should have average-case constant runtime
Popular implementations use hashing
11.38 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 void wordCounting () unordered_map <string , size_t > word_count; for (string word; cin >> word; ++word_count[word]); for (const auto &w : word_count) cout << w.first << " occurs " << w.second << (w.second > 1 ? "times" : "time" ) << endl ; } void wordTransformation () ifstream ifs_map ("../data/word_transformation.txt" ) ; ifstream ifs_content ("../data/given_to_transform.txt" ) ; if (!ifs_map || !ifs_content) { cerr << "can't find the documents." << endl ; return ; } unordered_map <string , string > trans_map; for (string key, value; ifs_map >> key && getline(ifs_map, value); ) if (value.size() > 1 ) trans_map[key] = value.substr(1 ).substr(0 , value.find_last_not_of(' ' )); for (string text, word; getline(ifs_content, text); cout << endl ) for (istringstream iss(text); iss >> word; ) { auto map_it = trans_map.find(word); cout << (map_it == trans_map.cend() ? word : map_it->second) << " " ; } } int main () wordTransformation(); }
第十二章 12.1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 StrBlob b1 { StrBlob b2 = {"a" , "an" , "the" }; b1 = b2; b2.push_back("about" ); }
12.2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 class StrBlob { public : using size_type = vector <string >::size_type; StrBlob():data(make_shared<vector <string >>()) { } StrBlob(initializer_list <string > il):data(make_shared<vector <string >>(il)) { } size_type size () const { return data->size(); } bool empty () const return data->empty(); } void push_back (const string &t) void pop_back () check(0 , "pop_back on empty StrBlob" ); data->pop_back(); } string & front () { check(0 , "front on empty StrBlob" ); return data->front(); } string & back () { check(0 , "back on empty StrBlob" ); return data->back(); } const string & front () const { check(0 , "front on empty StrBlob" ); return data->front(); } const string & back () const { check(0 , "back on empty StrBlob" ); return data->back(); } private : void check (size_type i, const string &msg) const { if (i >= data->size()) throw out_of_range(msg); } private : shared_ptr <vector <string >> data; };
12.3 可以但没必要
12.4 i 是 unsigned 的
12.5 Pros
The compiler will not use this constructor in an automatic conversion .
We can realize clearly which class we have used.
Cons
We always uses the constructor to construct a temporary StrBlob object .
cannot use the copy form of initialization with an explicit constructor. not easy to use.
12.6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 auto fun () return new vector <int >{}; } auto read (vector <int >* vec) for (int i; cin >> i; vec->push_back(i)); return vec; } void print (vector <int >* vec) for (auto i : *vec) cout << i <<" " ; delete vec; } int main () print(read(fun)); return 0 ; }
12.7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 auto fun () return make_shared<vector <int >>(); } auto read (share_ptr<vector <int >> vec) for (int i; cin >> i; vec->push_back(i)); return vec; } void print (share_ptr<vector <int >> vec) for (auto i : *vec) cout << i <<" " ; } int main () print(read(fun)); return 0 ; }
12.8 1 2 3 4 5 bool b () int * p = new int ; return p; }
12.9 1 2 3 4 int *q = new int (42 ), *r = new int (100 );r = q; auto q2 = make_shared<int >(42 ), r2 = make_shared<int >(100 );r2 = q2;
12.10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 void process (shared_ptr <int > ptr) cout << "inside the process function:" << ptr.use_count() << "\n" ; } int main () shared_ptr <int > p(new int (42 )); process(shared_ptr <int >(p)); cout << p.use_count() << "\n" << *p << "\n" ; return 0 ; }
12.11 函数内部可能会将 p 指向的内存释放,避免这种写法
12.12 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 void process (shared_ptr <int > ptr) cout << "inside the process function:" << ptr.use_count() << "\n" ; } int main () auto p = new int (); auto sp = make_shared<int >(); process(sp); process(new int ()); process(p); process(std ::shared_ptr <int >(p)); return 0 ; }
12.13 1 2 3 auto sp = make_shared<int >();auto p = sp.get();delete p;
12.14 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ;struct connection { string ip; int port; connection(string ip_, int port_):ip(ip_), port(port_){ } }; struct destination { string ip; int port; destination(string ip_, int port_):ip(ip_), port(port_){ } }; connection connect (destination* pDest) shared_ptr <connection> pConn(new connection(pDest->ip, pDest->port)); cout << "creating connection(" << pConn.use_count() << ")" << endl ; return *pConn; } void disconnect (connection pConn) cout << "connection close(" << pConn.ip << ":" << pConn.port << ")" << endl ; } void end_connection (connection *pConn) disconnect(*pConn); } void f (destination &d) connection conn = connect(&d); shared_ptr <connection> p(&conn, end_connection); cout << "connecting now(" << p.use_count() << ")" << endl ; } int main () destination dest ("202.118.176.67" , 3316 ) ; f(dest); }
12.15 1 2 3 shared_ptr <connection> p(&conn, [](connection *pConn){ disconnect(*pConn); });
12.16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <memory> using std ::string ; using std ::unique_ptr ;int main () unique_ptr <string > p1(new string ("string" )); std ::cout << *p1 << std ::endl ; p1.reset(nullptr ); }
12.17 & 12.18 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <memory> int main () int ix = 1024 , *pi = &ix, *pi2 = new int (2048 ); typedef std ::unique_ptr <int > IntP; return 0 ; }
12.19 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 class StrBlobPtr ;class StrBlob { public : using size_type = vector <string >::size_type; friend class StrBlobPtr ; StrBlobPtr begin () ; StrBlobPtr end () ; StrBlob() : data(std ::make_shared<vector <string >>()) {} StrBlob(std ::initializer_list <string > il) : data(std ::make_shared<vector <string >>(il)) {} size_type size () const { return data->size(); } bool empty () const return data->empty(); } void push_back (const string &t) void pop_back () { check(0 , "pop_back on empty StrBlob" ); data->pop_back(); } std ::string &front () { check(0 , "front on empty StrBlob" ); return data->front(); } std ::string &back () { check(0 , "back on empty StrBlob" ); return data->back(); } const std ::string &front () const { check(0 , "front on empty StrBlob" ); return data->front(); } const std ::string &back () const { check(0 , "back on empty StrBlob" ); return data->back(); } private : void check (size_type i, const string &msg) const { if (i >= data->size()) throw std ::out_of_range(msg); } private : std ::shared_ptr <vector <string >> data; }; class StrBlobPtr { public : StrBlobPtr() : curr(0 ) {} StrBlobPtr(StrBlob &a, size_t sz = 0 ) : wptr(a.data), curr(sz) {} bool operator !=(const StrBlobPtr &p) { return p.curr != curr; } string &deref () const { auto p = check(curr, "dereference past end" ); return (*p)[curr]; } StrBlobPtr &incr () { check(curr, "increment past end of StrBlobPtr" ); ++curr; return *this ; } private : std ::shared_ptr <vector <string >> check(size_t i, const string &msg) const { auto ret = wptr.lock(); if (!ret) throw std ::runtime_error("unbound StrBlobPtr" ); if (i >= ret->size()) throw std ::out_of_range(msg); return ret; } std ::weak_ptr<vector <string >> wptr; size_t curr; }; StrBlobPtr StrBlob::begin() { return StrBlobPtr(*this ); } StrBlobPtr StrBlob::end() { return StrBlobPtr(*this , data->size()); }
12.20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 int main () ifstream ifs ("../data/book.txt" ) ; StrBlob blob; for (string str;getline(ifs,str);) blob.push_back(str); for (StrBlobPtr pbeg(blob.begin()), pend(blob.end()); pbeg != pend; pbeg.incr()) cout << pbeg.deref() <<endl ; }
12.21 这样写不好读,还是原版好
12.22 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 class ConstStrBlobPtr { public : ConstStrBlobPtr() : curr(0 ) {} ConstStrBlobPtr(const StrBlob &a, size_t sz = 0 ) : wptr(a.data), curr(sz) {} bool operator !=(ConstStrBlobPtr &p) { return p.curr != curr; } const string &deref () const { auto p = check(curr, "dereference past end" ); return (*p)[curr]; } ConstStrBlobPtr &incr () { check(curr, "increment past end of StrBlobPtr" ); ++curr; return *this ; } private : std ::shared_ptr <vector <string >> check(size_t i, const string &msg) const { auto ret = wptr.lock(); if (!ret) throw std ::runtime_error("unbound StrBlobPtr" ); if (i >= ret->size()) throw std ::out_of_range(msg); return ret; } std ::weak_ptr<vector <string >> wptr; size_t curr; }; ConstStrBlobPtr StrBlob::begin() const { return ConstStrBlobPtr(*this ); } ConstStrBlobPtr StrBlob::end() const { return ConstStrBlobPtr(*this , data->size()); } class ConstStrBlobPtr ;class StrBlob { friend class ConstStrBlobPtr ; ConstStrBlobPtr begin () const ; ConstStrBlobPtr end () const ; }
12.23 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <string.h> #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std ;int main () char s1[] = "hello," ; char s2[] = "world!" ; char *s = new char [strlen (s1) + strlen (s2) + 1 ](); strcat (s, s1); strcat (s, s2); cout << s << endl ; delete [] s; s = nullptr ; string str1("hello,"), str2("world!"); cout << str1 + str2 << endl ; return 0 ; }
12.24 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstring> using namespace std ;char *charUp (char *p, const size_t &oldSize, const size_t &newSize) char *newBlock = new char [newSize](); if (!p) return newBlock; memcpy (newBlock, p, oldSize); delete [] p; p = newBlock; return p; } int main () char ch, *str = nullptr ; constexpr size_t sizeSt = 24 ; size_t i = 0 , length = 0 ; while (cin >> ch >> noskipws && !isspace (ch)) { if (i == length) { length += sizeSt; str = charUp(str, i, length); if (!str) { cout << "Could not allocate memory!" << endl ; return -1 ; } } str[i++] = ch; } str[i] = '\0' ; cout << string (str) << endl ; delete [] str; str = nullptr ; return 0 ; }
12.25 12.26 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <memory> using namespace std ;const int n = 5 ;int main () allocator<string > a; auto const p = a.allocate(n); string s; auto q = p; while (q != p + n && cin >> s) a.construct(q++, s); int count = 0 ; while (q != p) { count++; cout << *--q << endl ; a.destroy(q); } a.deallocate(p, n); cout << count << endl ; return 0 ; }
12.27 & 12.30 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <set> #include <memory> #include <sstream> #include <algorithm> #include <fstream> #include <ctype.h> using namespace std ;class QueryResult ;class TextQuery { public : using LineNo = vector <string >::size_type; TextQuery(ifstream &); QueryResult query (const string &) const ; private : shared_ptr <vector <string >> input; map <string , shared_ptr <set <LineNo>>> result; }; class QueryResult { public : friend ostream &print (ostream &, const QueryResult &) QueryResult(string s, shared_ptr <set <TextQuery::LineNo>> ns, shared_ptr <vector <string >> in) : word(s), nos(ns), input(in){}; private : string word; shared_ptr <set <TextQuery::LineNo>> nos; shared_ptr <vector <string >> input; }; TextQuery::TextQuery(ifstream &infile) : input(new vector <string >) { LineNo lineNo{0 }; for (string line; getline(infile, line); lineNo++) { input->push_back(line); istringstream s_line (line) for (string text, word; s_line >> text; word.clear()) { remove_copy_if(text.begin(), text.end(), back_inserter(word), ptr_fun<int , int >(&std ::ispunct )); auto &nos = result[word]; if (!nos) nos.reset(new set <LineNo>); nos->insert(lineNo); } } } QueryResult TextQuery::query(const string &str) const { static shared_ptr <set <LineNo>> nodata(new set <LineNo>); auto found = result.find(str); if (found == result.end()) return QueryResult(str, nodata, input); else return QueryResult(str, found->second, input); } ostream &print (ostream &out, const QueryResult &qr) out << qr.word << " occurt: " << qr.nos->size() << " " << (qr.nos->size() > 1 ? "times" : "time" ) << endl ; for (auto i : *qr.nos) cout << "\t(line " << i + 1 << ") " << qr.input->at(i) << endl ; return out; } void runQuery (ifstream &infile) TextQuery tq (infile) ; while (1 ) { cout << "Please input a word to look for, or 'q' to quit\n" ; string s; if (!(cin >> s) || s == "q" ) break ; print(cout , tq.query(s)) << endl ; } } int main () ifstream ifs ("D:/WorkSpace/C++/data.txt" ) ; runQuery(ifs); return 0 ; }
12.28 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <set> #include <memory> #include <sstream> #include <algorithm> #include <fstream> #include <ctype.h> using namespace std ;int main () ifstream ifs ("D:/WorkSpace/C++/data.txt" ) ; vector <string > input; map <string , set <decltype (input.size())>> dict; decltype (input.size()) lineNo{0 }; for (string line; getline(ifs, line); lineNo++) { input.push_back(line); istringstream s_line (line) for (string text, word; s_line >> text; word.clear()) { remove_copy_if(text.begin(), text.end(), back_inserter(word), ptr_fun<int , int >(&std ::ispunct )); dict[word].insert(lineNo); } } while (1 ) { cout << "Please input a word to look for, or 'q' to quit\n" ; string s; if (!(cin >> s) || s == "q" ) break ; auto found = dict.find(s); if (found == dict.end()) cout << s << " occurt: " << 0 << " " << "time" << endl ; else { cout << s << " occurt: " << found->second.size() << " " << (found->second.size() > 1 ? "times" : "time" ) << endl ; for (auto i : found->second) cout << "\t(line " << i + 1 << ") " << input.at(i) << endl ; } cout << endl ; } return 0 ; }
12.29 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 do { cout << "Please input a word to look for, or 'q' to quit\n" ; string s; if (!(cin >> s) || s == "q" ) break ; print(cout , tq.query(s)) << endl ; }while (1 );
12.31 vector代替set后,同一行多次出现的单词会重复进入存储空间,使用set能使得序列中同一元素唯一
12.32 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <set> #include <memory> #include <sstream> #include <algorithm> #include <fstream> #include <ctype.h> using namespace std ;class ConstStrBlobPtr ;class StrBlobPtr ;class StrBlob { public : using size_type = vector <string >::size_type; friend class StrBlobPtr ; friend class ConstStrBlobPtr ; ConstStrBlobPtr begin () const ; ConstStrBlobPtr end () const ; StrBlobPtr begin () ; StrBlobPtr end () ; StrBlob() : data(std ::make_shared<vector <string >>()) {} StrBlob(std ::initializer_list <string > il) : data(std ::make_shared<vector <string >>(il)) {} size_type size () const { return data->size(); } bool empty () const return data->empty(); } void push_back (const string &t) void pop_back () { check(0 , "pop_back on empty StrBlob" ); data->pop_back(); } std ::string &front () { check(0 , "front on empty StrBlob" ); return data->front(); } std ::string &back () { check(0 , "back on empty StrBlob" ); return data->back(); } const std ::string &front () const { check(0 , "front on empty StrBlob" ); return data->front(); } const std ::string &back () const { check(0 , "back on empty StrBlob" ); return data->back(); } private : void check (size_type i, const string &msg) const { if (i >= data->size()) throw std ::out_of_range(msg); } private : std ::shared_ptr <vector <string >> data; }; class StrBlobPtr { public : StrBlobPtr() : curr(0 ) {} StrBlobPtr(StrBlob &a, size_t sz = 0 ) : wptr(a.data), curr(sz) {} bool operator !=(const StrBlobPtr &p) { return p.curr != curr; } string &deref () const { auto p = check(curr, "dereference past end" ); return (*p)[curr]; } StrBlobPtr &incr () { check(curr, "increment past end of StrBlobPtr" ); ++curr; return *this ; } private : std ::shared_ptr <vector <string >> check(size_t i, const string &msg) const { auto ret = wptr.lock(); if (!ret) throw std ::runtime_error("unbound StrBlobPtr" ); if (i >= ret->size()) throw std ::out_of_range(msg); return ret; } std ::weak_ptr<vector <string >> wptr; size_t curr; }; class ConstStrBlobPtr { public : ConstStrBlobPtr() : curr(0 ) {} ConstStrBlobPtr(const StrBlob &a, size_t sz = 0 ) : wptr(a.data), curr(sz) {} bool operator !=(ConstStrBlobPtr &p) { return p.curr != curr; } const string &deref () const { auto p = check(curr, "dereference past end" ); return (*p)[curr]; } ConstStrBlobPtr &incr () { check(curr, "increment past end of StrBlobPtr" ); ++curr; return *this ; } private : std ::shared_ptr <vector <string >> check(size_t i, const string &msg) const { auto ret = wptr.lock(); if (!ret) throw std ::runtime_error("unbound StrBlobPtr" ); if (i >= ret->size()) throw std ::out_of_range(msg); return ret; } std ::weak_ptr<vector <string >> wptr; size_t curr; }; StrBlobPtr StrBlob::begin() { return StrBlobPtr(*this ); } StrBlobPtr StrBlob::end() { return StrBlobPtr(*this , data->size()); } ConstStrBlobPtr StrBlob::begin() const { return ConstStrBlobPtr(*this ); } ConstStrBlobPtr StrBlob::end() const { return ConstStrBlobPtr(*this , data->size()); } class QueryResult ;class TextQuery { public : TextQuery(ifstream &); QueryResult query (const string &) const ; private : StrBlob input; map <string , shared_ptr <set <StrBlob::size_type>>> result; }; class QueryResult { public : friend ostream &print (ostream &, const QueryResult &) QueryResult(const string &s, shared_ptr <set <StrBlob::size_type>> ns, const StrBlob &in) : word(s), nos(ns), input(in){}; private : string word; shared_ptr <set <StrBlob::size_type>> nos; StrBlob input; }; TextQuery::TextQuery(ifstream &infile) { StrBlob::size_type lineNo{0 }; for (string line; getline(infile, line); ++lineNo) { input.push_back(line); istringstream s_line (line) for (string text, word; s_line >> text; word.clear()) { remove_copy_if(text.begin(), text.end(), back_inserter(word), ptr_fun<int , int >(&std ::ispunct )); auto &nos = result[word]; if (!nos) nos.reset(new set <StrBlob::size_type>); nos->insert(lineNo); } } } QueryResult TextQuery::query(const string &str) const { static shared_ptr <set <StrBlob::size_type>> nodata(new set <StrBlob::size_type>); auto found = result.find(str); if (found == result.end()) return QueryResult(str, nodata, input); else return QueryResult(str, found->second, input); } ostream &print (ostream &out, const QueryResult &qr) out << qr.word << " occurt: " << qr.nos->size() << " " << (qr.nos->size() > 1 ? "times" : "time" ) << endl ; for (auto i : *qr.nos) { ConstStrBlobPtr p (qr.input, i) ; cout << "\t(line " << i + 1 << ") " << p.deref() << endl ; } return out; } void runQuery (ifstream &infile) TextQuery tq (infile) ; while (1 ) { cout << "Please input a word to look for, or 'q' to quit\n" ; string s; if (!(cin >> s) || s == "q" ) break ; print(cout , tq.query(s)) << endl ; } } int main () ifstream ifs ("D:/WorkSpace/C++/data.txt" ) ; runQuery(ifs); return 0 ; }
12.33 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class QueryResult { using ResultIter = set <StrBlob::size_type>::iterator; public : friend ostream &print (ostream &, const QueryResult &) QueryResult(const string &s, shared_ptr <set <StrBlob::size_type>> ns, const StrBlob &in) : word(s), nos(ns), input(in){}; ResultIter begin () const { return nos->begin(); } ResultIter end () const { return nos->end(); } shared_ptr <StrBlob> get_file() const { return make_shared<StrBlob>(input); } private : string word; shared_ptr <set <StrBlob::size_type>> nos; StrBlob input; };
第十三章 13.1 拷贝构造函数是第一个参数是当前类的引用,其它参数都有默认值的函数
当拷贝初始化发生:
使用 = 定义一个变量
将对象作为参数传给非引用类型形参
从非引用类型返回值的函数返回对象
用花括号列表(List Initialization)初始化聚合类的成员或者数组中的元素
某些类类型还会为所分配的对象使用拷贝初始化
13.2 1 2 Sales_data::Sales_data(Sales_data rhs);
13.3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 short count () return data.use_count(); } int main () StrBlob str ({ "hello" , "world" }) ; cout << "before: " << str.count() << endl ; StrBlob str_cp (str) ; cout << "after: " << str.count() << endl ; StrBlobPtr p (str) ; cout << "before: " << p.count() << endl ; StrBlobPtr p_cp (p) ; cout << "after: " << p.count() << endl ; }
13.4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Point global; Point foo_bar (Point arg) Point local = arg, *heap = new Point(global); *heap = local; Point pa[ 4 ] = { local, *heap }; return *heap; }
13.5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class HasPtr { public : HasPtr(const string &s = string ()) : ps(new string (s)), i(0 ) {} HasPtr(const HasPtr &hp) : ps(new string (*hp.ps)), i(ps.i) {} private : string *ps; int i; };
13.6
拷贝赋值运算符是函数,通常命名为 operator= , 参数与类相同
当赋值时发生
合成拷贝赋值运算符如果不是 private 等禁止状态,则会将右侧相应成员赋值给左侧
当该类没有定义自己的拷贝赋值运算符
13.7 都会浅拷贝, use_count 会发生与 13.3 一样的情况
13.8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <set> #include <memory> #include <sstream> #include <algorithm> #include <fstream> #include <ctype.h> using namespace std ;class HasPtr { public : HasPtr(const string &s = string ()) : ps(new string (s)), i(0 ) {} HasPtr(const HasPtr &hp) : ps(new string (*hp.ps)), i(hp.i) {} HasPtr &operator =(const HasPtr &right) { if (this != &right) { string *s = new string (*right.ps); delete ps; ps = s; i = right.i; } return *this ; } void pr () { cout << *ps << endl ; } void change (string a) { *ps = a; } private : string *ps; int i; }; int main () HasPtr a("world"), b; a.pr(), b.pr(); b = a; a.change("hello" ); a.pr(), b.pr(); getchar(); return 0 ; }
13.9
析构函数是类名以 ~ 为前缀的成员函数
对某些类可以放进 private 里控制类禁止被销毁,一般函数体内就是空的
当类没有定义自己的析构函数的时候
13.10
StrBlob :use_count 递减,如果动态对象已经没有 shared_ptr 的指向,则销毁StrBlobPtr :直接销毁,指向对象不析构
13.11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class HasPtr { public : HasPtr(const string &s = string ()) : ps(new string (s)), i(0 ) {} ~HasPtr() { delete ps; } HasPtr(const HasPtr &hp) : ps(new string (*hp.ps)), i(hp.i) {} HasPtr &operator =(const HasPtr &right) { if (this != &right) { string *s = new string (*right.ps); delete ps; ps = s; i = right.i; } return *this ; } void pr () { cout << *ps << endl ; } void change (string a) { *ps = a; } private : string *ps; int i; };
13.12 1 2 3 4 5 6 bool fun (const Sales_data *trans, Sales_data accum) Sales_data item1(*trans), item2(accum); return item1.isbn() != item2.isbn(); }
13.13 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <set> #include <memory> #include <sstream> #include <algorithm> #include <fstream> #include <ctype.h> using namespace std ;struct X { X() { cout << "X()" << endl ; } X(const X &) { cout << "X(const X&)" << endl ; } X &operator =(const X &) { cout << "X& operator=" << endl ; return *this ; } ~X() { cout << "~X()" << endl ; } }; void f (const X &rx, X x) vector <X> vec; vec.reserve(2 ); vec.push_back(rx); vec.push_back(x); } int main () X *ps = new X; X a; *ps = a; f(*ps, *ps); delete ps; getchar(); return 0 ; }
13.14 1 2 3 4 5 void f (numbered s) cout << s.mysn <<endl ; }numbered a, b = a, c = b; f(a); f(b); f(c);
13.15 拷贝构造函数会生成新的序号,最后会输出三个不同的序号,并且并非是我们想要的 a, b, c的编号,因为进入 f() 时还会进行一次拷贝构造
13.16 会改变,因为 f() 传参不用调用拷贝构造函数了,此次输出的序号就是我们想要的 a, b, c的编号
13.17 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <iostream> class numbered { public : numbered() { mysn = unique++; } numbered(const numbered &temp) { mysn = unique++; } int mysn; static int unique; }; int numbered::unique = 10 ;void f (const numbered &s) std ::cout << s.mysn << std ::endl ; } int main () numbered a, b = a, c = b; f(a); f(b); f(c); getchar(); return 0 ; }
13.18 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 #include <iostream> #include <string> class Employee { std ::string name; int id; static int num; public : Employee(); Employee(std ::string s = "Me" ) : name(s) { id = num++; } void print () { std ::cout << id << " " << name << std ::endl ; } }; int Employee::num = 10 ;int main () Employee a; Employee b; a.print(); b.print(); getchar(); return 0 ; }
13.19 1 2 3 4 Employee(const Employee&) = delete ; Employee& operator =(const Employee&) = delete ;
13.20 TextQuery 和 QueryResult 的成员是用智能指针来管理动态内存,因此当我们拷贝、赋值或销毁类对象的时候引用计数会发生改变乃至被销毁
13.21 不需要,因为 TextQuery 和 QueryResult 的成员是用智能指针来管理动态内存的
13.22 & 13.23 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class HasPtr { public : HasPtr(const string &s = string ()) : ps(new string (s)), i(0 ) {} ~HasPtr() { delete ps; } HasPtr(const HasPtr &hp) : ps(new string (*hp.ps)), i(hp.i) {} HasPtr &operator =(const HasPtr &right) { string *s = new string (*right.ps); delete ps; ps = s; i = right.i; return *this ; } private : string *ps; int i; };
13.24 没有析构函数,合成的析构函数将不会释放内存
没有构造拷贝函数,合成的函数将默认使用指针赋值,两个指针将指向同一个对象
13.25 两个函数需要在拷贝的时候新开内存给智能指针,而不是共享对象,不用析构函数是因为智能指针会自动在合成析构函数中被释放,如果 use_count() 为 0 的话
13.26 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class StrBlob { ... StrBlob(const StrBlob &sb) : data(make_shared<vector <string >>(*sb.data)) {} StrBlob &operator =(const StrBlob &sb) { data = make_shared<vector <string >>(*sb.data); return *this ; }; ... }
13.27 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class HasPtr { HasPtr(const string &s = string ()) : ps(new string (s)), i(0 ), use(new size_t (1 )){} HasPtr(const HasPtr &p) : ps(p.ps), i(p.i), use(p.use){++*use;} HasPtr& operator =(const HasPtr& rhs){ ++*rhs.use; if (--*use == 0 ){ delete ps; delete use; } ps = rhs.ps; use = rhs.use; i = rhs.i; return *this ; } ~HasPtr(){ if (--*use == 0 ){ delete use; delete ps; } } private : string *ps; int i; size_t *use; };
13.28 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 class TreeNode { TreeNode() : value(string ()), count(0 ), left(nullptr ), right(nullptr ){} TreeNode(const string &s, int c) : value(s), count(c), left(nullptr ), right(nullptr ){} ~TreeNode(){ delete left; delete right; } TreeNode(const TreeNode &rhs) ; value(rhs.value), count(rhs.count){ if (rhs.left) left = new TreeNode(*rhs.left); if (rhs.right) right = new TreeNode(*rhs.right); } TreeNode &operator =(const TreeNode &rhs){ value = rhs.value; count = rhs.count; TreeNode *temp = nullptr ; if (rhs.left) temp = new TreeNode(*rhs.left); delete left; left = temp; temp = nullptr ; if (rhs.right) temp = new TreeNode(*rhs.right); delete right; right = temp; delete temp; return *this ; } private : string value; int count; TreeNode *left; TreeNode *right; }; class BinStrTree { BinStrTree(const TreeNode &t = TreeNode()) : root(new TreeNode(t)), use(new size_t (1 )){} BinStrTree(const BinStrTree &rhs) : root(new TreeNode(*rhs.root)), use(rhs.use){++*use;} ~BinStrTree(){ if (--*use == 0 ){ delete root; delete use; } } BinStrTree& operator =(const BinStrTree& rhs){ ++*rhs.use; if (--*use == 0 ){ delete use; delete root; } root = rhs.root; use = rhs.use; return *this ; } private : TreeNode *root; size_t *use; };
13.29 swap(lhs.ps, rhs.ps); : swap(string*, string*)
swap(lhs.i, rhs.i); : swap(int, int)
13.30 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class HasPtr { HasPtr(const string &s = string ()) : ps(new string (s)), i(0 ), use(new size_t (1 )) {} HasPtr(const HasPtr &p) : ps(p.ps), i(p.i), use(p.use) { ++*use; } HasPtr &operator =(const HasPtr &rhs) { ++*rhs.use; if (--*use == 0 ) { delete ps; delete use; } ps = rhs.ps; use = rhs.use; i = rhs.i; return *this ; } ~HasPtr() { if (--*use == 0 ) { delete use; delete ps; } } friend void swap (HasPtr &, HasPtr &) private : string *ps; int i; size_t *use; }; inline void swap (HasPtr &lhs, HasPtr &rhs) swap(lhs.ps, rhs.ps); swap(lhs.i, rhs.i); cout << "call swap(HasPtr& lhs, HasPtr& rhs)" << endl ; }
13.31 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <algorithm> using namespace std ;class HasPtr { public : HasPtr(const string &s = string ()) : ps(new string (s)), i(0 ), use(new size_t (1 )) {} HasPtr(const HasPtr &p) : ps(p.ps), i(p.i), use(p.use) { ++*use; } HasPtr &operator =(HasPtr rhs) { swap(*this , rhs); return *this ; } ~HasPtr() { if (--*use == 0 ) { delete use; delete ps; } } void show () const { cout << *ps << endl ; } friend bool operator <(const HasPtr &lhs, const HasPtr &rhs); friend void swap (HasPtr &, HasPtr &) private : string *ps; int i; size_t *use; }; inline void swap (HasPtr &lhs, HasPtr &rhs) swap(lhs.ps, rhs.ps); swap(lhs.i, rhs.i); cout << "call swap(HasPtr& lhs, HasPtr& rhs)" << endl ; } bool operator <(const HasPtr &lhs, const HasPtr &rhs){ return *lhs.ps < *rhs.ps; } int main () HasPtr s{"s" }, a{"a" }, c{"c" }; vector <HasPtr> vec{s, a, c}; sort(vec.begin(), vec.end()); for (auto const &elem : vec) elem.show(); return 0 ; }
13.32 不会, swap 函数的益处本质在于交换指针而避免额外的内存开销,类指针的 HasPtr 版本就是指针交换
13.33 因为需要更改给定的 Floder 对象
13.34 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 class Message { friend class Folder ; friend void swap (Message &, Message &) friend std ::ostream& print (std ::ostream &, const Message &) ; public : explicit Message(const std::string &str = "") : content(str) {} Message(const Message &m) : content(m.content), folders(m.folders) { add_to_Folders(m); } Message& operator =(const Message &); ~Message() { remove_from_Folders(); } void save (Folder &) void remove (Folder &) private : std ::string content; std ::set <Folder *> folders; void add_to_Folders (const Message &) void remove_from_Folders () }; Message& Message::operator =(const Message &rhs) { remove_from_Folders(); content = rhs.content; folders = rhs.folders; add_to_Folders(rhs); return *this ; } void Message::save(Folder &f){ folders.insert(&f); f.addMsg(this ); } void Message::remove(Folder &f){ folders.erase(&f); f.remMsg(this ); } void Message::add_to_Folders(const Message &m){ for (auto f : m.folders) f->addMsg(this ); } void Message::remove_from_Folders(){ for (auto f : folders) f->remMsg(this ); } void swap (Message &lhs, Message &rhs) using std ::swap; for (auto f : lhs.folders) f->remMsg(&lhs); for (auto f : rhs.folders) f->remMsg(&rhs); swap(lhs.folders, rhs.folders); swap(lhs.content, rhs.content); for (auto f : lhs.folders) f->addMsg(&lhs); for (auto f : rhs.folders) f->addMsg(&rhs); } std ::ostream& print (std ::ostream &os, const Message &m) os << "content: " << m.content << '\n' ; for (const auto f : m.folders) std ::cout << f << ' ' ; return os; }
13.35 Floder 无法同步信息
13.36 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 #include <iostream> #include <set> #include <string> class Folder ;class Message { friend class Folder ; friend void swap (Message &, Message &) friend std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &, const Message &) ; public : explicit Message(const std::string &str = "") : content(str) {} Message(const Message &m) : content(m.content), folders(m.folders) { add_to_Folders(m); } Message &operator =(const Message &); ~Message() { remove_from_Folders(); } void save (Folder &) void remove (Folder &) private : std ::string content; std ::set <Folder *> folders; void add_to_Folders (const Message &) void remove_from_Folders () }; Message & Message::operator =(const Message &rhs) { remove_from_Folders(); content = rhs.content; folders = rhs.folders; add_to_Folders(rhs); return *this ; } class Folder { friend std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &, const Folder &) ; public : explicit Folder(const std::string &str = ".") : name(str) {} Folder(const Folder &f) : name(f.name), messages(f.messages) { add_to_Messages(f); } Folder &operator =(const Folder &); ~Folder() { remove_from_Messages(); } void addMsg (Message *m) void remMsg (Message *m) private : std ::string name; std ::set <Message *> messages; void add_to_Messages (const Folder &) void remove_from_Messages () }; Folder & Folder::operator =(const Folder &rhs) { remove_from_Messages(); name = rhs.name; messages = rhs.messages; add_to_Messages(rhs); return *this ; } void Folder::add_to_Messages(const Folder &f){ for (auto m : f.messages) m->folders.insert(this ); } void Folder::remove_from_Messages(){ for (auto m : messages) m->folders.erase(this ); } void Message::save(Folder &f){ folders.insert(&f); f.addMsg(this ); } void Message::remove(Folder &f){ folders.erase(&f); f.remMsg(this ); } void Message::add_to_Folders(const Message &m){ for (auto f : m.folders) f->addMsg(this ); } void Message::remove_from_Folders(){ for (auto f : folders) f->remMsg(this ); } void swap (Message &lhs, Message &rhs) using std ::swap; for (auto f : lhs.folders) f->remMsg(&lhs); for (auto f : rhs.folders) f->remMsg(&rhs); swap(lhs.folders, rhs.folders); swap(lhs.content, rhs.content); for (auto f : lhs.folders) f->addMsg(&lhs); for (auto f : rhs.folders) f->addMsg(&rhs); } std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &os, const Message &m) os << "content: " << m.content << '\n' ; for (const auto f : m.folders) std ::cout << f << ' ' ; return os; } std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &os, const Folder &f) os << "name: " << f.name << '\n' ; for (const auto m : f.messages) std ::cout << m << ' ' ; return os; } int main () Folder f ("InBox" ) ; Folder k ("New" ) ; Message a ("Hello, there!" ) ; a.save(f); a.save(k); print(std ::cout , a) << '\n' ; std ::cout << "folder f: " ; print(std ::cout , f) << '\n' ; std ::cout << "folder k: " ; print(std ::cout , k) << '\n' ; Folder x; x = k; std ::cout << "folder x: " ; print(std ::cout , x) << '\n' ; print(std ::cout , a) << '\n' ; return 0 ; }
13.37 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Message { friend class Folder ; friend void swap (Message &, Message &) friend std ::ostream &print (std ::ostream &, const Message &) ; public : explicit Message(const std::string &str = "") : content(str) {} Message(const Message &m) : content(m.content), folders(m.folders) { add_to_Folders(m); } Message &operator =(const Message &); ~Message() { remove_from_Folders(); } void save (Folder &) void remove (Folder &) void addFld (Folder *f) void remFld (Folder *f) private : std ::string content; std ::set <Folder *> folders; void add_to_Folders (const Message &) void remove_from_Folders () };
13.38 拷贝操作会多生成一个临时对象,这其中多出了一次构造和析构的调用;而交换操作参与的两个对象都需要进行删除、添加操作。这两种方式的效率都不如直接传入引用直接赋值。
13.39 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <memory> using namespace std ;class StrVec { public : StrVec() : elements(nullptr ), first_free(nullptr ), cap(nullptr ) {} ~StrVec() { free (); } StrVec(const StrVec &); StrVec &operator =(const StrVec &); void push_back (const string &) size_t size() const { return first_free - elements; } size_t capacity() const { return cap - elements; } string *begin () const return elements; } string *end () const return first_free; } void reserve (size_t ) void resize (size_t ) void resize (size_t , const string &s) private : static allocator<string > alloc; string *elements; string *first_free; string *cap; void free () void chk_n_alloc () { if (size() == capacity()) reallocate(); } pair<string *, string *> alloc_n_copy(const string *, const string *); void reallocate () void alloc_n_move (size_t ) }; void StrVec::push_back(const string &s){ chk_n_alloc(); alloc.construct(first_free++, s); } pair<string *, string *> StrVec::alloc_n_copy(const string *b, const string *e) { auto data = alloc.allocate(e - b); return {data, uninitialized_copy(b, e, data)}; } void StrVec::free (){ if (elements) { for (auto p = first_free; p != elements;) { alloc.destroy(p--); } alloc.deallocate(elements, cap - elements); } } StrVec::StrVec(const StrVec &s) { auto newdata = alloc_n_copy(s.begin(), s.end()); elements = newdata.first; first_free = cap = newdata.second; } StrVec &StrVec::operator =(const StrVec &rhs) { auto data = alloc_n_copy(rhs.begin(), rhs.end()); free (); elements = data.first; first_free = cap = data.second; return *this ; } void StrVec::alloc_n_move(size_t newcapacity){ auto newdata = alloc.allocate(newcapacity); auto dest = newdata; auto elem = elements; for (size_t i = 0 ; i != size(); i++) alloc.construct(dest++, std ::move(*elem++)); free (); elements = newdata; first_free = dest; cap = elements + newcapacity; } void StrVec::reallocate(){ auto newcapacity = size() ? 2 * size() : 1 ; alloc_n_move(newcapacity); } void StrVec::reserve(size_t newcapacity){ if (newcapacity <= capacity()) return ; alloc_n_move(newcapacity); } void StrVec::resize(size_t count){ resize(count, string ()); } void StrVec::resize(size_t count, const string &s){ if (count > size()) { if (count > capacity()) reserve(count * 2 ); for (size_t i = size(); i != count; i++) alloc.construct(first_free++, s); } else if (count < size()) { while (first_free != elements + count) alloc.destroy(--first_free); } }
13.40 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <memory> using namespace std ;class StrVec { public : StrVec(initializer_list <string >); private : void range_initialize (const string *, const string *) }; StrVec::StrVec(const StrVec &s) { range_initialize(s.begin(), s.end()); } StrVec::StrVec(initializer_list <string > ils) { range_initialize(ils.begin(), ils.end()); } void StrVec::range_initialize(const string *first, const string *last){ auto newdata = alloc_n_copy(first, last); elements = newdata.first; first_free = cap = newdata.second; }
13.41 first_free 指向最后一个元素的后一位,使用前置递增运算符正好填空,后置递增会导致留空。
13.42 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 #include <vector> #include <sstream> #include <fstream> #include <set> #include <string> #include <map> #include <initializer_list> #include <memory> #include <iostream> using namespace std ;class StrVec { public : StrVec() : elements(nullptr ), first_free(nullptr ), cap(nullptr ){}; StrVec(initializer_list <string > il) { auto data = alloc_n_copy(il.begin(), il.end()); elements = data.first; first_free = cap = data.second; } StrVec(const StrVec &); StrVec &operator =(const StrVec &); ~StrVec(); void push_back (const string &) size_t size() const { return first_free - elements; } size_t capacity() const { return cap - elements; } string *begin () const return elements; } string *end () const return first_free; } void reserve (size_t n) void resize (size_t n, const string &s = " " ) private : static allocator<string > alloc; void chk_n_alloc () { if (size() == capacity()) reallocate(); } pair<string *, string *> alloc_n_copy(const string *, const string *); void free () void reallocate () string *elements; string *first_free; string *cap; }; allocator<string > StrVec::alloc = allocator<string >(); pair<string *, string *> StrVec::alloc_n_copy(const string *b, const string *e) { auto data = alloc.allocate(e - b); return pair<string *, string *>(data, uninitialized_copy(e, b, data)); } void StrVec::free (){ if (elements) { auto b = first_free; while (b != elements) { alloc.destroy(--b); } alloc.deallocate(elements, cap - elements); } } void StrVec::reallocate(){ auto newcapacity = size() ? 2 * size() : 1 ; auto newdata = alloc.allocate(newcapacity); auto dest = newdata; auto elem = elements; for (size_t i = 0 ; i < size(); i++) { alloc.construct(dest++, move(*elem++)); } elements = newdata; first_free = dest; cap = elements + newcapacity; } StrVec::StrVec(const StrVec &s) { auto data = alloc_n_copy(s.begin(), s.end()); elements = data.first; first_free = cap = data.second; } StrVec &StrVec::operator =(const StrVec &rhs) { auto data = alloc_n_copy(rhs.begin(), rhs.end()); free (); elements = data.first; first_free = cap = data.second; return *this ; } void StrVec::push_back(const string &s){ chk_n_alloc(); alloc.construct(first_free++, s); } StrVec::~StrVec() { free (); } void StrVec::reserve(size_t n){ if (n < size()) return ; auto newcapacity = n; auto newdata = alloc.allocate(newcapacity); auto dest = newdata; auto elem = elements; for (size_t i = 0 ; i < size(); i++) { alloc.construct(dest++, move(*elem++)); } elements = newdata; first_free = dest; cap = elements + newcapacity; } void StrVec::resize(size_t n, const string &s){ if (n > size()) { if (n > capacity()) { reserve(n); } for (size_t i = size(); i < n; ++i) { alloc.construct(first_free++, s); } } else if (n < size()) { while ((elements + n) != first_free) { alloc.destroy(--first_free); } } } class QueryResult ;class TextQuery { friend class QueryResult ; shared_ptr <StrVec> file; map <string , set <int >> lineNum; public : TextQuery(ifstream &input) { int num = 0 ; string line; file = make_shared<StrVec>(); while (getline(input, line)) { file->push_back(line); istringstream s (line) string temp; while (s >> temp) { lineNum[temp].insert(num); } num++; } } QueryResult query (const string &str) ; }; class QueryResult { friend ostream &print (ostream &os, const QueryResult &q) shared_ptr <StrVec> lines; shared_ptr <set <int >> lineNum; string word; public : QueryResult(TextQuery &t, const string &s) { word = s; lineNum = make_shared<set <int >>(t.lineNum[s]); lines = t.file; } }; ostream &print (ostream &os, const QueryResult &q) if (q.lineNum->size() == 0 ) { cout << "Not found the word" ; return os; } cout << q.word << "occurs" << q.lineNum->size() << (q.lineNum->size() > 1 ? "times" : "time" ) << endl ; for (auto i : *(q.lineNum)) { os << "(Line number " << i << " ) " << *(q.lines->begin() + i) << endl ; } return os; } QueryResult TextQuery::query(const string &str) { return QueryResult(*this , str); } void runQueries (ifstream &infile) TextQuery tq (infile) ; while (true ) { cout << "Enter word to look for,or q to quit:" ; string s; if (!(cin >> s) || s == "q" ) break ; print(cout , tq.query(s)) << endl ; } } int main () ifstream text ("C:/surface/data/1342.txt" ) ; runQueries(text); }